API Reference
The Recharge API is primarily a REST API with some RPC endpoints to support common operations. It has predictable, resource-oriented URLs, accepts JSON-encoded request bodies, returns JSON-encoded responses, and uses standard HTTP response codes, authentication, and methods.
Related guides: Generate API tokens, Using the API
API and Platforms compatibility
Recharge offers hosted solutions and integrates with various ecommerce platforms to process recurring transactions with the setup of your choice. In order to be compatible with those platforms some of our API resources and endpoints may be limited in use to a subset of platforms. When that is the case we will flag with the help of tags the checkout/platform association for which that feature is compatible.
When there is no restriction of compatibility no tags will appear.
Below is a legend of the tags you may come across:
| Tag | Checkout solution | Ecommerce platform |
|---|---|---|
| BigCommerce | Recharge hosted | BigCommerce |
| Custom | Recharge hosted or API-first | Custom |
| RCS | Recharge hosted | Shopify |
| SCI | Shopify hosted | Shopify |
You may also come across other tags specifying regional restrictions (e.g. USA Only) or new releases (e.g. Alpha, Beta).
https://api.rechargeapps.comAuthentication
Recharge uses API keys to authenticate requests.
Each request to the API should contain an API token in the following header:
X-Recharge-Access-Token:store_api_token
Replace store_api_token with your API key.
All requests must be made over HTTPS.
API Token Scopes
Scopes can be set up from the API token edit page in Recharge to control the level of access of an API token.
The API currently supports the scopes below:
| Write | Read |
|---|---|
read_accounts |
|
write_batches |
read_batches |
write_customers |
read_customers |
write_discounts |
read_discounts |
read_events |
|
write_notifications |
|
write_orders |
read_orders |
write_payment_methods |
read_payment_methods |
write_products |
read_products |
write_subscriptions |
read_subscriptions |
read_store |
|
read_credit_accounts |
|
read_credit_adjustments |
curl -i -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-X GETVersioning
All requests will use your account API settings, unless you send a X-Recharge-Version header to specify the version.
You can use the same token to make calls to all versions. When no version is specified it will default to the default version on your store.
| Existing API Versions | Release notes |
|---|---|
2021-11 |
2021-11 release notes |
2021-01 |
Responses
Recharge uses conventional HTTP response codes to indicate the success or failure of an API request. In general, codes in the 2xx range indicate success, codes in the 4xx range indicate an error that failed given the information provided ( e.g. a required parameter was omitted, a charge failed, etc ), and codes in the 5xx range indicate an error with Recharge’s servers.
200 - OK: Everything worked as expected.
201 - OK: The request was successful, created a new resource, and resource created is in the body.
202 - OK: The request has been accepted and is in processing.
204 - OK: The server has successfully fulfilled the request and there is no content to send in the response body.
400 - Bad Request: The request was unacceptable, often due to a missing required parameter.
401 - Unauthorized: No valid API key was provided.
402 - Request Failed: The parameters were valid but the request failed.
403 - The request was authenticated but not authorized for the requested resource (permission scope error).
403 - Uninstalled Store.
404 - Not Found: The requested resource doesn’t exist.
405 - Method Not Allowed: The method is not allowed for this URI.
406 - The request was unacceptable, or requesting a data source which is not allowed although permissions permit the request.
409 - Conflict: You will get this error when you try to send two requests to edit an address or any of its child objects at the same time, in order to avoid out of date information being returned.
415 - The request body was not a JSON object.
422 - The request was understood but cannot be processed due to invalid or missing supplemental information.
426 - The request was made using an invalid API version.
429 - The request has been rate limited.
500 - Internal server error.
501 - The resource requested has not been implemented in the current version but may be implemented in the future.
503 - A 3rd party service on which the request depends has timed out.Extending responses
Our API endpoints and webhooks allow developers to extend responses with additional data in order to optimize calls, allowing for simpler and more efficient implementations.
The API supports including additional objects when using a GET request to retrieve a list or a GET request to retrieve a record by a specific id. This is achieved by using an include query parameter in the request URL. The include value contains the object or objects you want to include in the response of your request. On routes where multiple includes are available, you are able to pass multiple values separated by a comma (include=customer,metafields). The below table defines available include values for commonly used resources of the API.
Webhooks support included_objects on the topics listed below. Webhook included_objects accepts an array of supported values ("included_objects": [ "customer", "metafields"]). Specifying included_objects will return an enriched payload, containing the original resource and the associated included objects.
| Resource | Endpoints | Webhook topics | Supported include values |
Supported included_objects values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Addresses |
GET /addressesGET /addresses/:id |
address/createdaddress/updated |
customerdiscountpayment_methods (beta)subscriptions |
customermetafields |
Charges |
GET /chargesGET /charges/:id |
charge/createdcharge/failedcharge/max_retries_reachedcharge/paidcharge/refundedcharge/uncapturedcharge/upcomingcharge/updated |
metafields |
metafields |
Customers |
GET /customersGET /customers/:id |
customer/activatedcustomer/createdcustomer/deactivatedcustomer/payment_method_updatedcustomer/updated |
addressesmetafieldspayment_methods (beta)subscriptions |
addressesmetafields |
Orders |
GET /ordersGET /orders/:id |
order/cancelledorder/createdorder/deletedorder/processedorder/upcomingorder/updated |
customermetafieldssubscriptions |
customermetafields |
Products |
GET /productsGET /products/:id |
product/createdproduct/deletedproduct/updated |
collectionsmetafields |
collectionsmetafields |
Subscriptions |
GET /subscriptionsGET /subscriptions/:id |
subscription/activatedsubscription/cancelledsubscription/createdsubscription/deletedsubscription/skippedsubscription/updatedsubscription/unskippedsubscription/paused |
addressmetafields |
metafields |
Page Based Pagination
By default API calls will return 50 results. By using the limit parameter that can be increased to 250 results.
When there are more results than can fit on a page you may loop through the results by using the page parameter.
To request a page, include page as a parameter in the url.
E.g. https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions?limit=250&page=1
The example to the right shows a loop through all Subscription by page.
With minor changes this example can be used for looping through any object type: Customers, Addresses etc.
# request the first page (page=1)
curl -i -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-X GET https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions?limit=250&page=1
# request next page of results (page=2)
curl -i -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-X GET https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions?limit=250&page=2id: 123
id: 456
# ... continues through 250 records
page: 1 result_size: 250
id: 567
id: 678
# ... continues through 250 records
page: 2 result_size: 250
id: 567
id: 678
# ... continues through only 10 records, no further pages needed
page: 3 result_size: 10Cursor Pagination
By default API calls will return 50 results. By using the limit parameter that can be increased to 250 results. When there are more results than the current limit a cursor may be used to request additional results.
Cursor based pagination is the preferred method for looping through all records in a given data set, as it is more performant than specifying a page number along with number of results. This method also provides more assurance that you will receive all of the records in a given set.
Cursor based pagination works by providing a reference to a specific item in a list of sequential data which will represent the cursor, such as a numeric id. You can then specify whether you would like to query records starting before or starting after that item.
For convenience, the API provides a Link header in all responses for which there are further pages. This header contains both a next_cursor and previous_cursor link, which is just a URL with an encoded page_info parameter that contains any filters from your first call, as well as markers to let the API know where it left off and where to begin for the next call.
Please note that the only compatible filter allowed to be used with cursors is limit.
Supported endpoints for Link |
|---|
GET /addresses |
GET /async_batches |
GET /async_batches/:id/tasks |
GET /charges |
GET /customers |
GET /discounts |
GET /orders |
GET /products |
GET /subscriptions |
/charges requests which supply either the updated_at_min or created_at_min filter will not currently return a Link header.Requests which contain a filter for ids,
shopify_product_ids will not return a Link header.URL="https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges?limit=5"
response=$(curl -s -w "%{http_code}"
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-H 'X-Recharge-Version: 2021-11'
-X GET $URL)
content=$(sed '$ d' <<< "$response") # get all but the last line which contains the status code
# Display results
echo $content | jq "."
# parse next url
echo "Next URL"
next_cursor=$(jq ".next_cursor" <<< "${content}")
# Notice next_cursor value is passed as page_info query param
echo "$URL&page_info=$next_cursor"Sorting
The API supports sorting of results when using a GET request to retrieve a list. Sorting is achieved using a sort_by query parameter in the request URL. The sort_by value contains the parameter and sort direction for your results (ascending or descending), and available sort_by values vary between resources. The below table defines available sort_by options for commonly used resources.
| Resource | Supported sort_by_values |
|---|---|
Address |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc |
Async Batch |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc created_at-asc created_at-desc |
Charge |
Default: id-asc Options: id-asc id-desc created_at-asc created_at-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc charge_date-asc charge_date-desc |
Customer |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc created_at-asc created_at-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc |
Discount |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc created_at-asc created_at-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc |
Metafield |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc |
Onetime |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc created_at-asc created_at-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc |
Order |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc created_at-asc created_at-desc shipped_date-asc shipped_date-desc shipping_date-asc shipping_date-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc |
Product |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc created_at-asc created_at-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc title-asc title-desc |
Subscription |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc created_at-asc created_at-desc updated_at-asc updated_at-desc |
Webhook |
Default: id-desc Options: id-asc id-desc |
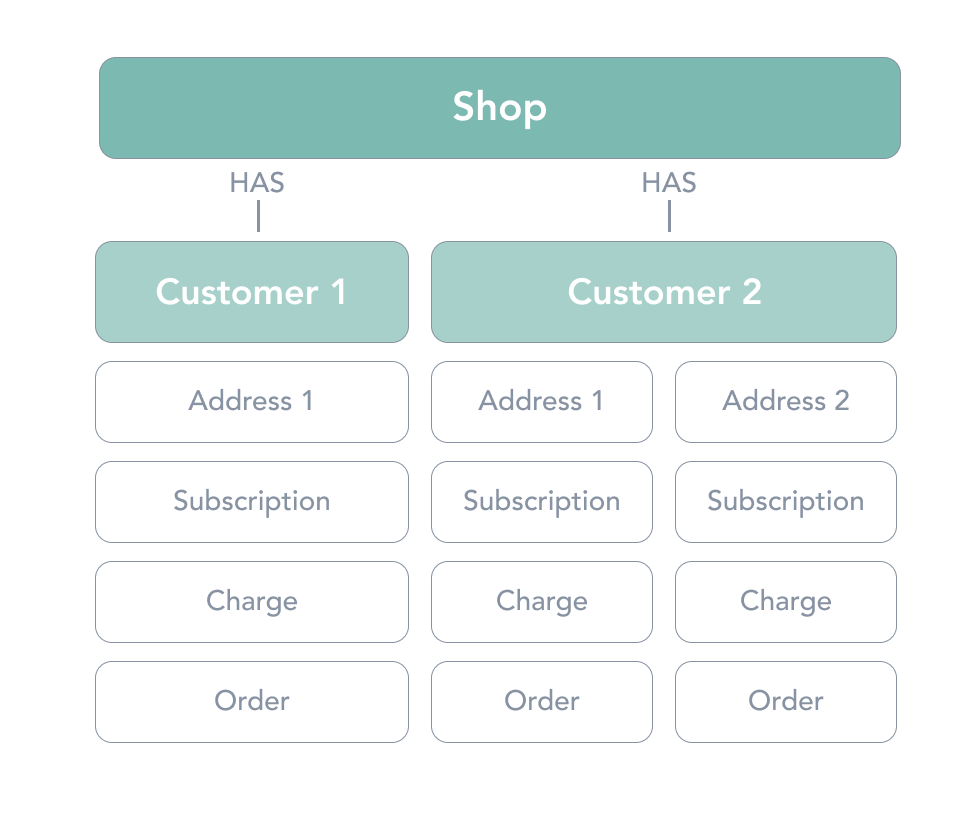
Addresses
Addresses represents one of the many shipping locations a customer may have. Subscriptions are tied to a given address. Each customer can have multiple address objects (many to one aka n:1) in the relationship. 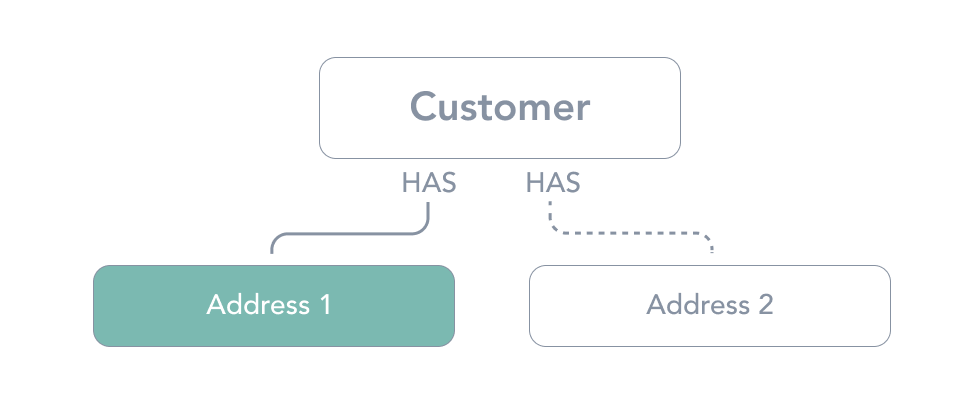
The address object
Addresses represents one of the many shipping locations a customer may have. Subscriptions are tied to a given address. Each customer can have multiple address objects (many to one aka n:1) in the relationship.
Attributes
- idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the
Address. - address1string
The street associated with the
Address. - address2string
Any additional information associated with the shipping address.
The note that that will be passed to the
notefield ofOrdersmade within theAddress.cart_noteis not currently honored when sent to the Shopify contract api (SCI).- citystring
The city associated with the shipping address.
- companystring
The company associated with the shipping address.
- countrystring
The country associated with the shipping address.
- country_codestring
The 2-letter country code.
- customer_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the
Customerassociated with theAddress. - discount_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier of
Discountthat is applied on theAddress. - first_namestring
The customer’s first name associated with the address.
- last_namestring
The customer’s last name associated with the address.
- note_attributesarray
Extra information that is added to the order.
Show object attributes - phonestring
The phone number associated with the address.
Presentment currency is the currency used to display prices to the associated on a storefront and at checkout.
Only set if the currency is different from the store-level currency. Else, will default to store-level currency.
- provincestring
The state or province associated with the address.
- shipping_lines_overridearray
Used when shipping rates need to be overridden. If this parameter has value
null, rates will be fetched when a relatedChargeis created or regeneratedShow object attributes - zipstring
The zip or postal code associated with the address.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
- cart_attributesarray
Additional information added to an initial order.
Important: This field will be deprecated. Please use
note_attributesinstead. - created_atdatetime
The date and time when the address was created.
- original_shipping_lines
Shipping line details.
Important: This field will be deprecated. Please use
shipping_lines_overrideinstead. - updated_atdatetime
The date and time when the
Addresswas last updated.
{
"address": {
"id": 21317826,
"address1": "1776 Washington Street",
"address2": "",
"cart_note": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"country_code": "US",
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:00:01",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_id": null,
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"note_attributes": [
{
"name": "custom name",
"value": "custom value"
}
],
"original_shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"phone": "5551234567",
"presentment_currency": null,
"province": "California",
"shipping_lines_override": null,
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:00:01",
"zip": "90404"
}
}Create an address
Create a new address for a customer.
Body Parameters
- address1string* Required
The street associated with the
Address. Minimum length is 1 character. If country is “United States” then validate with UPS external service. - address2string
Any additional information associated with the shipping address.
- cart_notestring
The note that that will be passed to the
notefield ofOrdersmade within theAddress.cart_noteis not currently honored when sent to the Shopify contract api (SCI). - citystring* Required
The city associated with the shipping address. Minimum length is 1 character. If country is “United States” then validate with UPS external service.
- companystring
The company associated with the shipping address.
- countrystring* Required
The country associated with the shipping address. Minimal length is 1 character. Check if the store supports shipping to this country. This is set by the merchant in their Shipping Settings page.
- first_namestring* Required
The customer’s first name associated with the address. Minimum length is 1 character.
- last_namestring* Required
The customer’s last name associated with the address. Minimum length is 1 character.
- note_attributesarray
Extra information that is added to the order.
Show object attributes - phonestring* Required
The phone number associated with the address. Must be included in the request schema but can be an empty string.
- presentment_currencystring
The currency that charges on this address will be processed in. If no presentment_currency is passed, it will be set to your default store currency.
- provincestring* Required
The state or province associated with the address. Check if country requires a province
COUNTRIES_REQUIRING_PROVINCE. If country isUnited Statesthen validate with UPS external service. - shipping_lines_overridearray
Used when shipping rates need to be overridden. If this parameter has value
null, rates will be fetched when a relatedChargeis created or regeneratedShow object attributes - zipstring* Required
The zip or postal code associated with the address. Check if the country requires a zip code
COUNTRIES_NOT_REQUIRING_ZIP. If not included in the list then a zip code with the minimum length of 1 character is required. If the country isUnited Statesthen validate against regexUNITED_STATES_ZIP_REGEXand validate with UPS external service. If country isUnited Kingdomthen validate against regexUNITED_KINGDOM_ZIP_REGEX.
More Parameters
- cart_attributesarray
Additional information added to an initial order.
Important note: This field will be deprecated. Please use
note_attributesinstead. - original_shipping_lines
Shipping line details.
Important note: This field will be deprecated. Please use
shipping_lines_overrideinstead.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers/3411137/addresses' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"address1": "1776 Washington Street",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"note_attributes": [
{
"name": "custom name",
"value": "custom value"
}
],
"phone": "5551234567",
"presentment_currency": "USD",
"province": "California",
"shipping_lines_override": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"zip": "90404"
}'{
"address": {
"id": 21317826,
"address1": "1776 Washington Street",
"address2": "",
"cart_note": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"country_code": "US",
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:00:01",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_id": null,
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"note_attributes": [
{
"name": "custom name",
"value": "custom value"
}
],
"shipping_lines_override": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"phone": "5551234567",
"presentment_currency": "USD",
"province": "California",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:00:01",
"zip": "90404"
}
}Retrieve an address
Retrieves address for customer based on specified address id.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/21317826' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"address": {
"id": 21317826,
"address1": "6419 Ocean Front Walk",
"address2": "Apt 1",
"cart_note": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "",
"country": "United States",
"country_code": "US",
"created_at": "2020-06-16T12:45:35",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"discount_id": null,
"first_name": "Nikola",
"last_name": "Tesla",
"note_attributes": [
{
"name": "custom name",
"value": "custom value"
}
],
"original_shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"phone": "1-800-800-8000",
"presentment_currency": null,
"province": "California",
"shipping_lines_override": null,
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T11:12:58",
"zip": "90293"
}
}Update an address
Updates an existing address to match the specified parameters.
When updating the country property you will have to update the zip property as well, otherwise you will receive an error.
Body Parameters
- address1string
The street associated with the
Address. Minimum length is 1 character. If country is “United States” then validate with UPS external service. - address2string
Any additional information associated with the shipping address.
The note that that will be passed to the
notefield ofOrdersmade within theAddress.cart_noteis not currently honored when sent to the Shopify contract api (SCI).- citystring
The city associated with the shipping address. Minimum length is 1 character. If country is “United States” then validate with UPS external service.
- companystring
The company associated with the shipping address.
- countrystring
The country associated with the shipping address. Minimal length is 1 character. Check if the store supports shipping to this country. This is set by the merchant in their Shipping Settings page.
- first_namestring
The customer’s first name associated with the address. Minimum length is 1 character.
- last_namestring
The customer’s last name associated with the address. Minimum length is 1 character.
- note_attributesarray
Extra information that is added to the order.
Show object attributes - phonestring
The phone number associated with the address. Must be included in the request schema but can be an empty string.
- provincestring
The state or province associated with the address. Check if country requires a province
COUNTRIES_REQUIRING_PROVINCE. If country isUnited Statesthen validate with UPS external service. Used when shipping rates need to be overridden. If this parameter has value
null, rates will be fetched when a relatedChargeis created or regeneratedShow object attributes- zipstring
The zip or postal code associated with the address. Check if the country requires a zip code
COUNTRIES_NOT_REQUIRING_ZIP. If not included in the list then a zip code with the minimum length of 1 character is required. If the country isUnited Statesthen validate against regexUNITED_STATES_ZIP_REGEXand validate with UPS external service. If country isUnited Kingdomthen validate against regexUNITED_KINGDOM_ZIP_REGEX.
More Parameters
- cart_attributesarray
Additional information added to an initial order.
Important note: This field will be deprecated. Please use
note_attributesinstead. - original_shipping_lines
Shipping line details.
Important note: This field will be deprecated. Please use
shipping_lines_overrideinstead.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X PUT 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/21317826' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"address1": "3020 Nebraska Avenue"}'{
"address": {
"id": 21317826,
"address1": "3020 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"cart_note": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"country_code": "US",
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:00:01",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_id": null,
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"note_attributes": [
{
"name": "custom name",
"value": "custom value"
}
],
"original_shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"phone": "5551234567",
"presentment_currency": null,
"province": "California",
"shipping_lines_override": null,
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:00:01",
"zip": "90404"
}
}Delete an address
It is possible to delete certain addresses from the store using API. However, there are some rules for deleting them. Note: Only Addresses with no active subscriptions can be deleted.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/21317826' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List addresses
Returns all addresses from the store, or addresses for the user given in the parameter.
HTTPS request examples
GET /addresses GET /customers/:id/addresses
You can combine created_at_min and created_at_max to return all addresses created in the given timespan. This also applies to updated_at_min and updated_at_max parameters
Query Parameters
- created_at_maxstring
Returns addresses created before the given time.
- created_at_minstring
Returns addresses created after the given time.
- customer_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the customer associated with the address.
- discount_codestring
Returns addresses that have the provided discount_code.
- discount_idstring
Returns addresses that have the provided discount_id.
- idsstring
Filter addresses by id. If passing multiple values, must be comma separated. Non-integer values will result in a 422 error
- limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
The amount of results. Default is 50 while the maximum is 250.
- pagestring*Deprecated
Default: 1
The page to show. Default is 1.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
- updated_at_maxstring
Returns addresses updated before the given date.
- updated_at_minstring
Returns addresses updated after the given time.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d limit=3 -G{
"addresses": [
{
"id": 48563471,
"address1": "6419 Ocean Front Walk",
"address2": "Apt 1",
"cart_note": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "",
"country": "United States",
"country_code": "US",
"created_at": "2020-06-16T12:45:35",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"discount_id": null,
"first_name": "Nikola",
"last_name": "Tesla",
"note_attributes": [
{
"name": "custom name",
"value": "custom value"
}
],
"original_shipping_lines": [],
"phone": "1-800-800-8000",
"presentment_currency": null,
"province": "California",
"shipping_lines_override": null,
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T11:12:58",
"zip": "90293"
}
]
}Count addresses
Retrieve the count of addresses.
HTTPS request examples
GET /addresses/count GET /addresses/count?discount_code=10PERCENTOFF GET /addresses/count?discount_id=123123123 GET /addresses/count?created_at_min=2019-11-11 GET /addresses/count?created_at_max=2019-11-11 GET /addresses/count?updated_at_min=2019-11-11 GET /addresses/count?updated_at_max=2019-11-11 GET /addresses/count?created_at_min=2019-11-10&updated_at_max=2019-11-11
Notes: you can combine multiple parameters with &
Query Parameters
- created_at_maxstring
Returns addresses created before the given time.
- created_at_minstring
Returns addresses created after the given time.
- discount_codestring
Returns addresses that have the provided discount_code.
- discount_idstring
Returns addresses that have the provided discount_id.
- updated_at_maxstring
Returns addresses updated before the given date.
- updated_at_minstring
Returns addresses updated after the given time.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/count' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"count": 6000
}Validate an address
USA only
It is important to validate an address before attempting to create charges for it, as at that point the user may no longer be available to edit incorrect values.
Address validation works only for USA addresses.
Body Parameters
- address1string* Required
The street associated with the address.
- citystring* Required
The city associated with the address.
- statestring* Required
The state associated with the address.
- zipcodestring* Required
The zip or postal code associated with the address.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/validate' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"address1": "1776 Washington Street",
"city": "santa monica",
"state": "California",
"zipcode": "90404"
}'{
"city": "santa monica",
"errors": {},
"state": "CA",
"state_name": "California",
"zipcode": "90404"
}Charges
A charge is the representation of a financial transaction linked to the purchase of an item (past or future). It can be a transaction that was processed already or the representation of an upcoming transaction. A charge is linked to its corresponding Orders( one Order for pay as you go subscriptions and several for pre-paid). Order are created once the corresponding Charge is successful. After successful payment, the first order will be immediately submitted to the external platform if applicable (e.g. Shopify, BigCommerce). 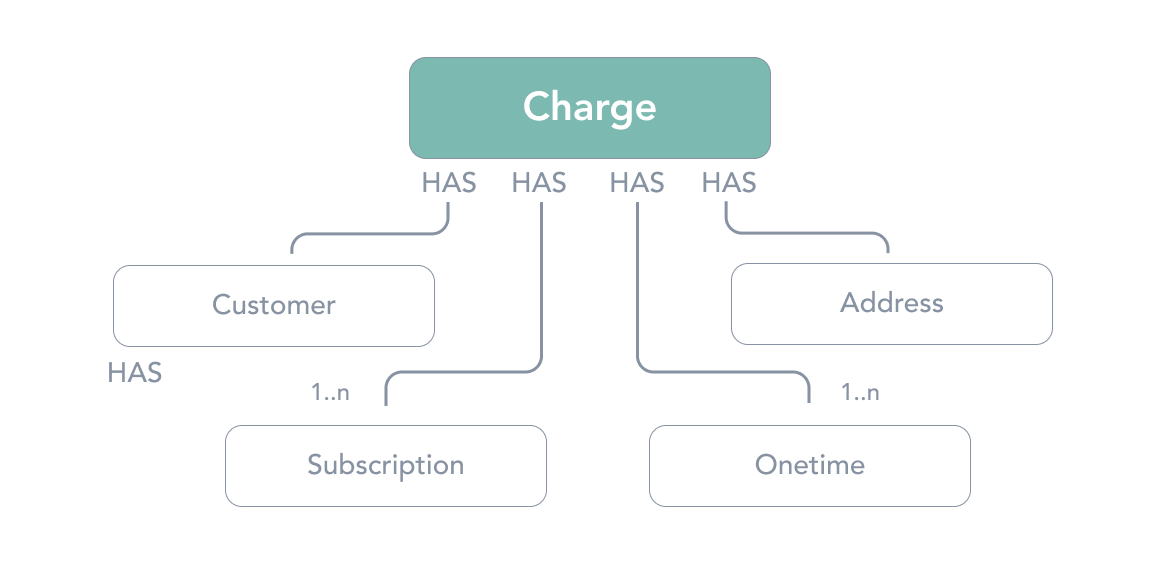
The charge object
A Charge is the representation of the financial transaction linked to a purchase (past or future). It can be a transaction that was processed already or the representation of an upcoming transaction. A charge is linked to its corresponding Orders (one for pay as you go subscriptions and several for pre-paid).
A Charge can have many parent subscriptions. All subscriptions on a given Address with the same next_charge_date date will be merged into one Charge and that charge will contain one line_item per Subscription.
Attributes
- idinteger
The unique numeric identifier for the charge.
- address_idinteger
The customer shipping address the charge is tied to.
- analytics_dataobject
An object containing analytics data associated with the charge.
Show object attributes - billing_addressobject
All the billing information related to the charge.
Show object attributes - client_detailsobject
Details of the access method used by the purchaser.
Show object attributes - created_atdatetime
When the
Chargewas created. - customer_hashstring
The
hashof theCustomerassociated with the charge. - customer_idstring
The
idof theCustomerassociated with the charge. - discount_codesobject
An array of discounts associated with the charge.
Show object attributes - emailstring
The email address of the customer.
- first_namestring
The first name of the customer.
- last_namestring
The last name of the customer.
- line_itemsarray
A list of
line_itemobjects, each one containing information about an item in the charge. Oneline_itemper subscription.Show object attributes - notestring
Shows the next order in sequence.
- note_attributesarray
note attributes.
Show object attributes - processor_namestring
The payment processor used on the charge.
- processed_atdatetime
The date and time when the transaction was processed.
- scheduled_atdatetime
When the charge processing will next be attempted.
If a charge failed to process,
scheduled_atremains the initial scheduled date of the processing not the date of the next attempt. - shipments_countinteger
The number of successfully processed child orders on the charge.
- shipping_addressobject
The shipping address of the shipping address.
Show object attributes - shipping_linesarray
An array of shipping lines associated with the charge.
Show object attributes - shopify_order_idinteger
The unique numeric identifier within Shopify for the charge
- statusstring
Possible values: SUCCESS, ERROR, QUEUED, SKIPPED, REFUNDED, PARTIALLY_REFUNDED
The status of the charge.
- subtotal_pricestring
The item price without taxes and shipping.
- tagsarray
Array of strings used to distinguish specific charges.
- tax_linesarray
Array of strings used to distinguish specific charges.
Show object attributes - total_discountsstring
The sum of the discounts applied to the
Charge. - total_line_items_pricestring
The sum of all the prices of all the items in the charge.
- total_pricestring
The sum of all the prices of all the items in the charge, taxes and discounts included (must be positive).
- total_refundsstring
The sum of all refunds that were made on specific charge.
- total_weightstring
The sum of all refunds that were made on specific charge.
- transaction_idstring
The unique alphanumeric identifier of the transaction.
- typestring
Possible values: CHECKOUT, RECURRING
The type of the charge.
- updated_atdatetime
The date and time when the
Chargewas last updated.
Error related attributes
- errorstring
Error reason as sentence text (typically returned direct from the payment processor). e.g.
"Customer needs to update credit card" - error_typestring
Structured reason why the charge failed such as
CUSTOMER_NEEDS_TO_UPDATE_CARD - last_charge_attempt_datedatetime
The date when a charge was last attempted.
- number_times_triedinteger
Shows how many times an attempt to charge was placed.
- retry_datedate
The date when the next attempt will be placed.
- shopify_variant_id_not_foundinteger
Indicates if Recharge was able to find the
shopify_variant_idfrom the charge.
More Attributes
- has_uncommited_changes
Specifies whether the charge is scheduled for a regeneration (if the subscription related to the charge was updated in the last 5 seconds using “commit_update”:false).
- sub_total
The item price without taxes and discounts. Use subtotal_price instead.
{
"charge": {
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "next order #1",
"note_attributes": [
{
"name": "custom name",
"value": "custom value"
}
],
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2018-12-12T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": 12345,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": 12,
"subtotal_price": "12:00",
"tags": "Subscription",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "cch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44"
}
}Retrieve a charge
Retrieve a charge using the Recharge charge id.
Starting March 19th, 2025, processed charges (those where status equals success, refunded, or partially-refunded) that have a value for processed_at greater than 90 days in the past will no longer appear in responses. As a result, you may receive an error.
Charge data processed over 90 days ago will remain available through the Exports tool in the Recharge merchant portal and within the Merchant portal UI.
Example of unaffected API calls:
[RETRIEVE A CHARGE] /charges/{id} (if it’s a charge that does not have a processed_at date or the processed_at date is within the last 90 days)
Example of API calls that will result in an error:
[RETRIEVE A CHARGE] /charges/{id} (if it’s a charge with a processed_at date older than 90 days)
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/100714428' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"charge": {
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "next order #1",
"note_attributes": [
{
"name": "custom name",
"value": "custom value"
}
],
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2018-12-12T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": 12345,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": 12,
"subtotal_price": "12:00",
"tags": "Subscription",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "cch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44"
}
}List charges
Returns a list of charges.
HTTPS request examples
GET /charges?address_id=21317826 GET /charges?customer_id=18819267 GET /charges?date_min=2021-05-18&date_max=2021-06-18 GET /charges?discount_code=10PERCENTOFF GET /charges?discount_id=753963GET /charges?ids=1123551,262667345,12341535 GET /charges?shopify_order_id=7895652 GET /charges?sort_by=id-desc GET /charges?status=queued GET /charges?status=queued,refunded,partially_refunded GET /charges?subscription_id=753489514
Starting March 19th, 2025, processed charges (those where status equals success, refunded, or partially- refunded) that have a value for processed_at greater than 90 days in the past will no longer appear in responses. As a result, you may receive a partial data set or an empty list.
Charge data processed over 90 days ago will remain available through the Exports tool in the Recharge merchant portal and within the Merchant portal UI.
Examples of unaffected API calls:
[LIST CHARGES] /charges?status=queued
[LIST CHARGES] /charges?status=error
Examples of API calls that may return partial results:
[LIST CHARGES] /charges?processed_at_min=2024-01-01 (this would only return results that have a processed_at date in the last 90 days)
[LIST CHARGES] /charges?status=success,queued (this would return all queued charges but only return success charges that have a processed_at date in the last 90 days)
Example of API calls that will result in an empty list:
[LIST CHARGES] /charges?processed_at_max=2024-01-01 (any date over 90 days old)
Reminder: returned charges are sorted ascending by id value by default.
Query Parameters
- address_idstring
Filter charges by address.
- created_at_maxstring
Show charges created before the given date.
- created_at_minstring
Show charges created after the given date.
- customer_idstring
Filter charges by customer.
- datestring
Show charges scheduled on the given date.
- date_maxstring
Show charges scheduled before the given date.
- date_minstring
Show charges scheduled after the given date.
- discount_codestring
List charges that contain the given
discount_code. - discount_idstring
List charges that contain the given
discount_id. - idsstring
Filter charges by
id. If passing multiple values, must be comma separated.Non-integer values will result in a
422error. - limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
The amount of results.
- pagestring*Deprecated
Default: 1
The page to show.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
- shopify_order_idstring
Filter charges by
shopify_order_id. - statusstring
Possible values: SUCCESS, QUEUED, ERROR, REFUNDED, PARTIALLY_REFUNDED, SKIPPED
Filter charges by status
- subscription_idstring
Filter charges by
subscription_id. - updated_at_maxstring
Show charges updated before the given date.
- updated_at_minstring
Show charges updated after the given date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d limit=3 -G{
"charges": [
{
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": " next order #1 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": null,
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2018-12-19T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": null,
"subtotal_price": "12:00",
"tags": "Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "cch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T10:08:14"
}
]
}Count charges
Retrieve a count of charges.
HTTPS request examples
GET /charges/count GET /charges/count?address_id=10175825 GET /charges/count?customer_id=10101 GET /charges/count?date_min=2019-11-10&date_max=2019-11-11 GET /charges/count?discount_code=10PERCENTOFF GET /charges/count?discount_id=18493516 GET /charges/count?shopify_order_id=281223307 GET /charges/count?status=queued GET /charges/count?status=queued,refunded,partially_refunded GET /charges/count?subscription_id=14562
Reminder: returned charges are sorted ascending by id value.
Query Parameters
- address_idstring
Filter charges by address.
- customer_idstring
Filter charges by customer.
- datestring
Show charges scheduled on the given date.
- date_maxstring
Show charges scheduled before the given date.
- date_minstring
Show charges scheduled after the given date.
- discount_idstring
List charges that contain the given discount_id.
- shopify_order_idinteger
Filter charges by shopify_order_id.
- statusstring
Filter charges by status. Available status: SUCCESS, QUEUED, ERROR, REFUNDED, PARTIALLY_REFUNDED, SKIPPED.
- subscription_idstring
Filter charges by subscription_id.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/count' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"count": 38667
}Change next charge date
Modify the next_charge_date of the subscription.
If there are two queued Charges with the same address_id, and you update their scheduled_at attribute to match, they will be merged into one Charge.
Body Parameters
- next_charge_datestring* Required
Next charge date in ISO 8601 format.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/100714428/change_next_charge_date' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"next_charge_date": "2021-12-19"}'{
"charge": {
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": " next order #1 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": null,
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2021-12-19T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": null,
"subtotal_price": "12.00",
"tags": "Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "cch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:59:28"
}
}Skip a charge
Skip the charge and generate the next Charge in the schedule.
When a Charge contains multiple line_items and you only want to skip the charge for a subset of items, you can specify the specific subscription_id OR subscriptions_ids.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/100714428/skip' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"subscription_ids": ["27363808"]}'{
"charge": {
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": " next order #1 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": null,
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2021-12-19T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": null,
"subtotal_price": "12.00",
"tags": "Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "cch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:59:28"
}
}Unskip a charge
Unskip the charge.
When a Charge contains multiple line_items and you only want to unskip the charge for a subset of items, you can specify the specific subscription_id OR subscriptions_ids.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object - 422
Unprocessable
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/100714428/unskip' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"subscription_ids": ["27363808"]}'{
"charge": {
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": " next order #1 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": null,
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2021-12-19T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": null,
"subtotal_price": "12.00",
"tags": "Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "cch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:59:28"
}
}Refund a charge
Applies a refund to a Charge.
After the refund, the Charge will have status parameter REFUNDED or PARTIALLY_REFUNDED.
Body Parameters
- amountstring* Required
Amount of money that will be refunded. It can be fully or partially refunded.
- full_refundboolean
If this parameter is set to
true, the charge will be totally refunded.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/100714428/refund' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"amount": 11.00}'{
"charge": {
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": " next order #1 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": null,
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2021-12-19T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": null,
"subtotal_price": "12.00",
"tags": "Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "cch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:59:28"
}
}Process a charge
Pro plan
The charge processing route can be used to process Charges that are in a queued or error status.
Related guides: Charges FAQ
The /charges/{id}/process endpoint is available to Recharge Pro merchants on a request basis. If you’re interested in leveraging the Recharge charge processing API, reach out to your account manager or our Support team.
Learn more about Recharge Pro.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/100714428/process' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{}'{
"charge": {
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": " next order #1 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": null,
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2021-12-19T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": null,
"subtotal_price": "12.00",
"tags": "Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "cch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T09:59:28"
}
}Capture a charge
Pro plan
Beta
If you are leveraging the authorize/capture workflow with Recharge, the charge/capture_payment endpoint is how to capture the funds of a previously authorized Charge.
Capture Window
You can only capture payment on charges that have been authorized within the last 7 days. This is a limitation of payment providers/financial institutions and Recharge cannot configure or override this limit. Any charges that are attempted to be captured beyond that 7 day window may respond in an error indicating the charge cannot be captured.
As a result, Recharge provides a
charge/uncaptured webhook. If subscribed, this webhook will notify you of any charges that are not captured 6 days after authorization. Please refer to the webhooks section for more information.
The capture_payment endpoint is available to Recharge Pro merchants in the Recharge Closed Beta group. If you’re interested in leveraging the Recharge charge capture_payment endpoint, reach out to your account manager or our Support team.
Learn more about Recharge Pro.
Responses
- 200
Charge captured successfully
Show response object - 400
Bad Request
Show response object - 404
Not Found
Show response object - 422
Unprocessable
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/100714428/capture_payment' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{}'{
"charge": {
"id": 100714428,
"address_id": 21317826,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"client_details": {
"browser_ip": null,
"user_agent": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-14T09:45:44",
"customer_hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 4536,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0175/0695/9460/products/Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "12.00",
"price": "12.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255183683",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844924611",
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 27363808,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "next order #2",
"note_attributes": null,
"processor_name": "stripe",
"scheduled_at": "2018-12-19T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": "",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": null,
"status": "SUCCESS",
"sub_total": null,
"subtotal_price": "12:00",
"tags": "Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": "0.0",
"total_line_items_price": "12.00",
"total_price": "12.00",
"total_refunds": "12.00",
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 4536,
"transaction_id": "ch_1Du2QpJ2iqHvZRd18RyqoPvc",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T10:08:14"
}
}Checkouts
The checkout resource allows to create unique checkout experiences.
We currently support Stripe, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Braintree as payment processor.
Related guides: Mobile payments
Important - The Checkout endpoints are only available for BigCommerce and Custom. Checkouts on Shopify must go through Shopify.
The checkout object
The checkout resource allows to create unique checkout experiences.
We currently support Stripe, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Braintree, Authorize as payment processor.
The Checkout endpoints are only available for BigCommerce and Custom implementations. Checkouts on Shopify must go through Shopify.
If you are using test stripe keys, you can use tok_visa as your token.
Attributes
- analytics_dataobject
Analytics data containing amongst other things the
utm_paramsShow object attributes - applied_discountobject
Details of the discount code applied to the checkout.
Show object attributes - billing_addressobject
Billing address for the checkout.
Show object attributes - buyer_accepts_marketingboolean
Serves as the audit trail for a buyer email marketing’s communication opt-in
- charge_idinteger
The
idassociated to theChargegenerated as a by-product of aCheckoutbeing processed.This value will remain
nullas long as theCheckouthas not been completed. - completed_attimestamp
The timestamp at which the
Checkoutwas processed.This value will remain
nullas long as theCheckouthas not been completed. - created_attimestamp
The timestamp at which the
Checkoutwas created. - currencystring
The presentment currency of the
Checkout.This will also be the currency of the resulting Address and Subscriptions created by the checkout processing.
- discount_codestring
Discount code to be used on the checkout, e.g. “DISCOUNT20”.
- emailstring
Email address for the customer.
- external_checkout_idstring
Field which will hold the value of the corresponding external checkout or cart if the checkout was branched from another platform.
- external_checkout_sourcestring
Possible values: big_commerce, headless, shopify
Source of the creation of the checkout.
- external_customer_idstring
Customer identifier in the source platform issuing the checkout.
This field is useful for mapping to your customer id in your central CRM, ERP or any other commerce platform where you maintain your customer’s profiles.
- line_itemsarray
The details of the different items being purchased by the user.
Show object attributes - notestring
Note used to store free text notes.
- note_attributesarray
Structured note attributes.
Show object attributes - payment_processorstring
Name of the payment processor selected for the checkout.
Will remain
nulluntil payment details have been filled in. - payment_processor_customer_idstring
Identifier for the customer on the payment processor platform.
Will remain
nulluntil the checkout has been processed. - payment_processor_transaction_idstring
Identifier for the transaction on the payment processor platform.
Will remain
nulluntil the checkout has been processed. - phonestring
Customer phone number.
- requires_shippingboolean
Signals if the
Orderresulting from the processing of the checkout will need to be shipped aka packed and delivered.This relies on whether any of the
line_itemsrequires_shipping. - shipping_addressobject
Shipping address for the checkout.
Show object attributes - shipping_address_validationsobject
Results of the shipping address validation.
only available once the shipping address has been filled in.
Show object attributes - shipping_linearray
Shipping lines.
Show object attributes - shipping_ratestring
The name of the shipping rate applied.
- tax_linesarray
Tax details.
Show object attributes - taxes_includedboolean
Whether taxes are included in the price of the line_items
- tokenstring
Unique identifier of the checkout. Used by the update and processing and update endpoints.
- total_pricestring
Total amount for the full checkout transaction
- total_taxstring
Total amount of tax for the full checkout transaction
- updated_attimestamp
The timestamp at which the
Checkoutwas last updated.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"checkout": {
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "textlink",
"utm_data_source": "shopify_cookie",
"utm_medium": "cpc",
"utm_source": "google",
"utm_term": "mleko",
"utm_timestamp": "2020-03-05T00:00:00"
}
]
},
"applied_discount": {
"amount": "7.50",
"applicable": true,
"non_applicable_reason": "",
"value": "7.50",
"value_type": "fixed_amount"
},
"billing_address": null,
"buyer_accepts_marketing": false,
"charge_id": null,
"completed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-07-10T09:21:46+00:00",
"currency": "USD",
"discount_code": "POPUS_25",
"email": "somerandomemail@test.com",
"external_checkout_id": "<cart_token>",
"external_checkout_source": "ecommerce_platform",
"line_items": [
{
"charge_interval_frequency": 5,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"first_recurring_charge_delay": null,
"fulfillment_service": "manual",
"grams": 1000,
"image": "//cdn.example.com/s/files/1/0279/8387/2103/products/kazan_small.jpg?v=1586451337",
"line_price": "30.00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": 5,
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"order_interval_unit_type": "day",
"original_price": "5.00",
"price": "5.00",
"product_id": 4546063663207,
"product_type": "Milk",
"properties": null,
"quantity": 6,
"recurring_price": "5.00",
"requires_shipping": true,
"sku": "kRaViCah-1",
"tax_code": null,
"taxable": false,
"title": "Powder Milk",
"type": "SUBSCRIPTION",
"variant_id": 32165284380775,
"variant_title": "1 / Powder",
"vendor": "Imlek"
}
],
"note": null,
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": null,
"payment_processor_customer_id": null,
"payment_processor_transaction_id": null,
"phone": null,
"requires_shipping": true,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "6419 Ocean Front Walk",
"address2": "Apt 2",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Novak",
"last_name": "Djokovic",
"phone": "1-800-800-8000",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90293"
},
"shipping_address_validations": {
"country_is_supported": true,
"ups": true
},
"shipping_line": null,
"shipping_rate": null,
"subtotal_price": "22.50",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"taxes_included": false,
"token": "b706eecfd66c45329d3886a02d7515d6",
"total_price": "22.50",
"total_tax": "0.00",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T09:21:46+00:00"
}
}Create a checkout
Endpoint to create a checkout object and start populating it.
Related guides: Checkout integrations
The Checkout endpoints are only available for BigCommerce and Custom. Checkouts on Shopify must go through Shopify.
The token field received on checkout POST response is the unique identifier for the Checkout. Use it to make updates to the Checkout.
Body Parameters
- analytics_dataobject
Analytics data containing amongst other things the
utm_params.analytics_datawill be added toSubscription,CustomerandChargeobjects created as a result of the successful processing of theCheckout.Show object attributes - billing_addressobject
Billing address for the checkout.
Show object attributes - buyer_accepts_marketingboolean
Serves as the audit trail for a buyer email marketing’s communication opt-in
- currencystring
The presentment currency of the
Checkout.Only currencies set up in the store setting
store_presentment_currenciesare accepted. This will also be the currency of the resulting Address and Subscriptions created by the checkout processing. - discount_codestring
Discount code to be used on the checkout, e.g. “DISCOUNT20”.
- emailstring
Email address for the customer.
will be required before being able to process a
Checkout. - external_checkout_idstring
Cart token from ecommerce platform.
- external_checkout_sourcestring
Possible values: big_commerce, headless, shopify
Ecommerce platform hosting the cart.
- external_checkout_customer_idstring
Ecommerce platform hosting the cart.
- line_itemsarray* Required
The details of the different items being purchased by the user.
will be required before being able to process a
Checkout.Show object attributes - notestring
Note used to store free text notes.
- note_attributesarray
Structured note attributes.
Show object attributes - phonestring
Customer phone number.
- shipping_addressobject
Shipping address for the checkout.
will be required before being able to process a
Checkout.Show object attributes
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object - 422
Unprocessable
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/checkouts' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "textlink",
"utm_data_source": "website_cookie",
"utm_medium": "cpc",
"utm_source": "google",
"utm_term": "mleko",
"utm_timestamp": "2020-03-05"
}]
},
"discount_code": "POPUS_25",
"email":"somerandomemail@test.com",
"external_checkout_id": "<cart_token>",
"external_checkout_source": "custom",
"line_items": [
{
"charge_interval_frequency": 5,
"cutoff_day_of_month": None,
"cutoff_day_of_week": None,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": None,
"fulfillment_service": "manual",
"order_day_of_month": None,
"order_day_of_week": None,
"order_interval_frequency": 5,
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"product_id": 4546063663207,
"quantity": 6,
"requires_shipping": True,
"taxable": True,
"variant_id": 32165284380775
}
],
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "6419 Ocean Front Walk",
"address2": "Apt 2",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Novak",
"last_name": "Djokovic",
"phone": "1-800-800-8000",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90293"
}
}'{
"checkout": {
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "textlink",
"utm_data_source": "website_cookie",
"utm_medium": "cpc",
"utm_source": "google",
"utm_term": "mleko",
"utm_timestamp": "2020-03-05T00:00:00"
}
]
},
"applied_discount": {
"amount": "7.50",
"applicable": true,
"non_applicable_reason": "",
"value": "7.50",
"value_type": "fixed_amount"
},
"billing_address": {
"address1": "6419 Ocean Front Walk",
"address2": "Apt 2",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Novak",
"last_name": "Djokovic",
"phone": "1-800-800-8000",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90293"
},
"buyer_accepts_marketing": false,
"charge_id": null,
"completed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-07-10T09:21:46.259352+00:00",
"currency": "USD",
"discount_code": "POPUS_25",
"email": "somerandomemail@test.com",
"external_checkout_id": "<cart_token>",
"external_checkout_source": "custom",
"external_customer_id": "someone",
"line_items": [
{
"charge_interval_frequency": 5,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"first_recurring_charge_delay": null,
"fulfillment_service": "manual",
"grams": 1000,
"handle": null,
"image": "//cdn.example.com/s/files/1/0279/8387/2103/products/kazan_small.jpg?v=1586451337",
"line_price": "30.00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": 5,
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"order_interval_unit_type": "day",
"original_price": "5.00",
"price": "5.00",
"product_id": 4546063663207,
"product_type": "Milk",
"properties": null,
"quantity": 6,
"recurring_price": "5.00",
"requires_shipping": true,
"sku": "kRaViCah-1",
"tax_code": null,
"taxable": false,
"title": "Powder Milk",
"type": "SUBSCRIPTION",
"variant_id": 32165284380775,
"variant_title": "1 / Powder",
"vendor": "Imlek"
}
],
"note": null,
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": null,
"payment_processor_customer_id": null,
"payment_processor_transaction_id": null,
"phone": null,
"requires_shipping": true,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "6419 Ocean Front Walk",
"address2": "Apt 2",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Novak",
"last_name": "Djokovic",
"phone": "1-800-800-8000",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90293"
},
"shipping_address_validations": {
"country_is_supported": true,
"ups": true
},
"shipping_line": null,
"shipping_rate": null,
"subtotal_price": "22.50",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"taxes_included": false,
"token": "b706eecfd66c45329d3886a02d7515d6",
"total_price": "22.50",
"total_tax": "1.28",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T09:21:46.284703+00:00"
}
}Retrieve a checkout
Retrieve a checkout
The Checkout endpoints are only available for BigCommerce and Custom. Checkouts on Shopify must go through Shopify.
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/checkouts/6a7c36a1213a4d7fb746e6588fa55005' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"checkout": {
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "textlink",
"utm_data_source": "website_cookie",
"utm_medium": "cpc",
"utm_source": "google",
"utm_term": "mleko",
"utm_timestamp": "2020-03-05T00:00:00"
}
]
},
"applied_discount": {
"amount": "7.50",
"applicable": true,
"non_applicable_reason": "",
"value": "7.50",
"value_type": "fixed_amount"
},
"billing_address": null,
"buyer_accepts_marketing": false,
"charge_id": null,
"completed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-07-10T09:21:46.259352+00:00",
"currency": "USD",
"discount_code": "POPUS_25",
"email": "somerandomemail@test.com",
"external_checkout_id": "<cart_token>",
"external_checkout_source": "headless",
"line_items": [
{
"charge_interval_frequency": 5,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"first_recurring_charge_delay": null,
"fulfillment_service": "manual",
"grams": 1000,
"image": "//cdn.example.com/s/files/1/0279/8387/2103/products/kazan_small.jpg?v=1586451337",
"line_price": "30.00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": 5,
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"order_interval_unit_type": "day",
"original_price": "5.00",
"price": "5.00",
"product_id": 4546063663207,
"product_type": "Milk",
"properties": null,
"quantity": 6,
"recurring_price": "5.00",
"requires_shipping": true,
"sku": "kRaViCah-1",
"tax_code": null,
"taxable": false,
"title": "Powder Milk",
"type": "SUBSCRIPTION",
"variant_id": 32165284380775,
"variant_title": "1 / Powder",
"vendor": "Imlek"
}
],
"note": null,
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": null,
"payment_processor_customer_id": null,
"payment_processor_transaction_id": null,
"phone": null,
"requires_shipping": true,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "6419 Ocean Front Walk",
"address2": "Apt 2",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Novak",
"last_name": "Djokovic",
"phone": "1-800-800-8000",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90293"
},
"shipping_address_validations": {
"country_is_supported": true,
"ups": true
},
"shipping_line": null,
"shipping_rate": null,
"subtotal_price": "22.50",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"taxes_included": false,
"token": "b706eecfd66c45329d3886a02d7515d6",
"total_price": "22.50",
"total_tax": "0.00",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T09:21:46.284703+00:00"
}
}Update a checkout
You can modify an existing checkout to match the specified parameters.
Related guides: Checkout integrations
The Checkout endpoints are only available for BigCommerce and Custom. Checkouts on Shopify must go through Shopify.
If you are using test stripe keys, you can use tok_visa as your token.
Body Parameters
- analytics_dataobject
Analytics data containing amongst other things the
utm_params.analytics_datawill be added toSubscription,CustomerandChargeobjects created as a result of the successful processing of theCheckout.Show object attributes - billing_addressobject
Billing address for the checkout.
Show object attributes - buyer_accepts_marketingboolean
Does the buyer accept marketing, newsletters etc.
- currencystring
The presentment currency of the
Checkout.Only currencies set up in the store setting
store_presentment_currenciesare accepted. This will also be the currency of the resulting Address and Subscriptions created by the checkout processing. - discount_codestring
Discount code to be used on the checkout, e.g. “DISCOUNT20”.
- emailstring
Email address for the customer.
- external_checkout_idstring
Cart token from ecommerce platform.
- external_checkout_sourcestring
Possible values: big_commerce, headless, shopify
Ecommerce platform hosting the cart.
- external_checkout_customer_idstring
Ecommerce platform hosting the cart.
- line_itemsarray
quantity,product_idandvariant_idare required parameters in line_items.Show object attributes - notestring
Note attribute used to store custom notes.
- note_attributesarray
Each array entry must contain a dictionary with “name” and “value” keys.
Show object attributes - partial_shippingboolean
When set to true, shipping address validations are reduced to only require country and zip when creating/updating a checkout. The full shipping address including address line 1 must be added to the checkout before processing associated charges. This is helpful for mobile payments.
Related guides: Mobile payments - phonestring
Customer phone number.
- shipping_addressobject
Shipping address for the checkout.
When using mobile payment options, insufficient shipping address data is available until payment intent, which causes validation errors when updating the checkout object.
Related guides: Checkout mobile paymentShow object attributes
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/checkouts/98ac7af0c9d447019379c6ccdb24d069' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"line_items": [
{
"product_id": 4546063663207,
"quantity": 6,
"variant_id": 3844924611
}
]
}'{
"checkout": {
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "textlink",
"utm_data_source": "website_cookie",
"utm_medium": "cpc",
"utm_source": "google",
"utm_term": "mleko",
"utm_timestamp": "2020-03-05T00:00:00"
}
]
},
"applied_discount": {
"amount": "7.50",
"applicable": true,
"non_applicable_reason": "",
"value": "7.50",
"value_type": "fixed_amount"
},
"billing_address": null,
"buyer_accepts_marketing": false,
"charge_id": null,
"completed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-07-10T09:21:46.259352+00:00",
"currency": "USD",
"discount_code": "POPUS_25",
"email": "somerandomemail@test.com",
"external_checkout_id": "<cart_token>",
"external_checkout_source": "headless",
"line_items": [
{
"charge_interval_frequency": 5,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"first_recurring_charge_delay": null,
"fulfillment_service": "manual",
"grams": 1000,
"image": "//cdn.example.com/s/files/1/0279/8387/2103/products/kazan_small.jpg?v=1586451337",
"line_price": "30.00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": 5,
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"order_interval_unit_type": "day",
"original_price": "5.00",
"price": "5.00",
"product_id": 4546063663207,
"product_type": "Milk",
"properties": null,
"quantity": 6,
"recurring_price": "5.00",
"requires_shipping": true,
"sku": "kRaViCah-1",
"tax_code": null,
"taxable": false,
"title": "Powder Milk",
"type": "SUBSCRIPTION",
"variant_id": 32165284380775,
"variant_title": "1 / Powder",
"vendor": "Imlek"
}
],
"note": null,
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": null,
"payment_processor_customer_id": null,
"payment_processor_transaction_id": null,
"phone": null,
"requires_shipping": true,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "6419 Ocean Front Walk",
"address2": "Apt 2",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": "",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Novak",
"last_name": "Djokovic",
"phone": "1-800-800-8000",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90293"
},
"shipping_address_validations": {
"country_is_supported": true,
"ups": true
},
"shipping_line": null,
"shipping_rate": null,
"subtotal_price": "22.50",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"taxes_included": false,
"token": "b706eecfd66c45329d3886a02d7515d6",
"total_price": "22.50",
"total_tax": "0.00",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T09:21:46.284703+00:00"
}
}Retrieve shipping rates
Retrieve all shipping rates for a specific checkout.
The Checkout endpoints are only available for BigCommerce and Custom. Checkouts on Shopify must go through Shopify.
Responses
- 200
success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/checkouts/6a7c36a1213a4d7fb746e6588fa55005/shipping_rates' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"shipping_rates": [
{
"checkout": {
"subtotal_price": "22.50",
"total_price": "42.40",
"total_tax": "0.00"
},
"code": "Standard",
"delivery_range": null,
"description": null,
"handle": "shopify-Standard-19.90",
"name": "Standard",
"phone_required": false,
"price": "19.90",
"tax_lines": [],
"title": "Standard"
}
]
}Process a checkout
You can process and charge checkout using our API.
The Checkout endpoints are only available for BigCommerce and Custom. Checkouts on Shopify must go through Shopify.
The Checkout API supports Stripe, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Braintree as payment processor.
If you are using test stripe keys, you can use tok_visa as your token. For checkouts using Mobile Payments, see Mobile Payments with Checkout API
Body Parameters
- payment_processorstring* Required
Possible values: stripe, braintree, mollie, authorize
The name of payment processor.
- payment_tokenstring* Required
Payment token that will be used in transaction.
For
stripethis field needs to be populated with a payment method.
Forbraintreethis field needs to be populated with a payment nonce.
Formolliethis field needs to be populated with a mandate. - payment_typestring
Possible values: CREDIT_CARD, PAYPAL, APPLE_PAY, GOOGLE_PAY
It identifies the payment type.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object - 422
Unprocessable
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/checkouts/5a5c19ea31c44641855017f1276db959/charge' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"payment_token": "<payment_token>",
"payment_type": "CREDIT_CARD"
}'{
"checkout_charge": {
"authorization_token": null,
"charge_id": 258065996,
"free": false,
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"payment_processor_customer_id": "cus_HcbgqiS49fABBg62E",
"payment_processor_transaction_id": "ch_1H3McXJ2zdqHvZaRd191xV2idRt",
"payment_token": "tok_visa",
"payment_type": "CREDIT_CARD",
"status": "successful"
}
}Customers
The Customer object holds account and billing information. Email is unique on the customer; no two customers for a store can have the same email. Address is the child of the customer object. There can be many child addresses on a customer, but only one parent customer per address. 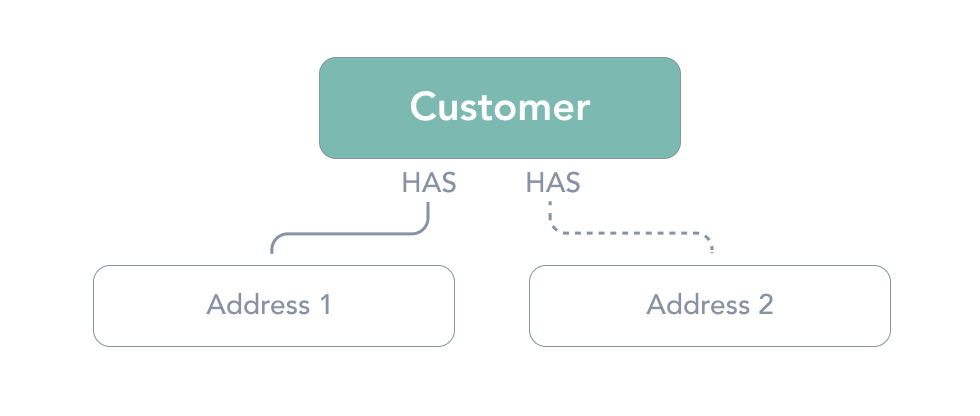
The customer object
The following fields are deprecated: stripe_customer_token, paypal_customer_token, authorizedotnet_profile_id, authorizedotnet_payment_profile_id. To add payment methods to a customer use 2021-11 /payment_methods instead
Attributes
- idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the customer.
- accepts_marketingboolean
Indicates whether the
Customergives consent for marketing communications. - billing_address1string
The customer’s billing address.
- billing_address2string
An additional field for the customer’s billing address.
- billing_citystring
The customer’s billing city.
- billing_companystring
The customer’s billing company.
- billing_countrystring
The customer’s billing country.
- billing_first_namestring
The customer’s billing first name. Required when creating a customer.
- billing_last_namestring
The customer’s billing last name. Required when creating a customer.
- billing_phonestring
The customer’s billing phone number.
- billing_provincestring
The customer’s billing province or state name.
- billing_zipstring
The customer’s billing zip or postal code.
- created_atdatetime
The date and time when the customer was created.
- emailstring
The email address of the customer.
- first_charge_processed_atstring
Date when first charge was processed for the customer.
- first_namestring
The customer’s first name.
- has_card_error_in_dunningboolean
Does have a credit card in dunning, can be
trueandfalse. - has_valid_payment_methodboolean
Is the payment method valid or not, can be
trueandfalse. - hashstring
The unique string identifier used in a customers portal link.
- last_namestring
The customer’s last name.
- number_active_subscriptionsinteger
The number of active subscriptions for the customer.
- number_subscriptionsinteger
The number of subscriptions for the customer.
- phonestring
The customer’s phone number.
- processor_typestring
What the merchant processor customer is stored on.
- reason_payment_method_not_validstring
Why payment method is not valid.
- shopify_customer_idstring
Shopify’s unique identifier for the customer.
- statusstring
Customer’s status, can be
ACTIVEandINACTIVE. - updated_atdatetime
The date and time when the customer was last updated.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"id": 18819267,
"accepts_marketing": true,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"billing_address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"billing_address2": null,
"billing_city": "Los Angeles",
"billing_company": null,
"billing_country": "United States",
"billing_phone": "3103843698",
"billing_province": "California",
"billing_zip": "90404",
"created_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38",
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_charge_processed_at": null,
"first_name": "Jacob",
"has_card_error_in_dunning": false,
"has_valid_payment_method": false,
"hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"last_name": "Bronowski",
"number_active_subscriptions": 0,
"number_subscriptions": 0,
"phone": "+16175551212",
"processor_type": null,
"reason_payment_method_not_valid": null,
"shopify_customer_id": null,
"status": "INACTIVE",
"stripe_customer_token": "cus_I9bJ...",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38"
}Create a customer in Recharge.
If you plan to add payment information, it must be the tokenized customer representation. We do not accept card data directly. Please make sure it starts with ‘cus’ and not with a 'tok’, as the 'cus’ is prefix for customer token, and 'tok’ is prefix for payment token.
Creating a customer in Recharge will not create the customer on any other platform at this time.
Write_Payments permission is only required when creating customers with payment token information, or updating payment token information on a customer.
Body Parameters
- accepts_marketingboolean
Indicates whether the
Customergives consent for marketing communications. - authorizedotnet_payment_profile_idinteger*Deprecated
Authorize.net customer payment profile id. Required when
authorizedotnet_profile_idis provided. - authorizedotnet_profile_idinteger*Deprecated
Authorize.net customer profile id. If both
authorizedotnet_profile_idandauthorizedotnet_payment_profile_idis provided the authorize.net payment profile will be tokenized and associated with the created customer. The tokenized value is returned as customer’s authorizedotnet_customer_token field. - billing_address1string* Required
The customer’s billing address 1.
- billing_address2string
An additional field for the customer’s billing address.
- billing_citystring* Required
The customer’s billing city.
- billing_companystring
The customer’s billing company.
- billing_countrystring* Required
The customer’s billing country.
- billing_first_namestring* Required
The customer’s billing first name.
- billing_last_namestring* Required
The customer’s billing last name.
- billing_phonestring
The customer’s billing phone number.
- billing_provincestring* Required
The customer’s billing province or state name.
- billing_zipstring* Required
The customer’s billing zip or postal code.
- emailstring* Required
The customer’s email address.
- first_namestring* Required
The customer’s first name.
- last_namestring* Required
The customer’s last name.
- paypal_customer_tokenstring*Deprecated
The payment processor customer payment token.
- phonestring
The customer’s phone number.
- processor_typestring
What the merchant processor customer is stored on.
- shopify_customer_idstring
The shopify customer id.
_The provided “shopify_customer_id” must match the provided “email” in the Shopify database for the customer. - stripe_customer_tokenstring*Deprecated
The customer token, you will need to tokenize customers first on the payment processors end, and after you get the customer token, you can create the Recharge customer with it.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"billing_address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"billing_city": "Los Angeles",
"billing_country": "United States",
"billing_first_name": "Mike",
"billing_last_name": "Flynn",
"billing_phone": "3103843698",
"billing_province": "California",
"billing_zip": "90404",
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"stripe_customer_token": "Customer_payment_token"
}'{
"customer": {
"id": 18819267,
"accepts_marketing": true,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"billing_address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"billing_address2": null,
"billing_city": "Los Angeles",
"billing_company": null,
"billing_country": "United States",
"billing_phone": "3103843698",
"billing_province": "California",
"billing_zip": "90404",
"created_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38",
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_charge_processed_at": null,
"first_name": "Mike",
"hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"has_card_error_in_dunning": false,
"has_valid_payment_method": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"number_active_subscriptions": 0,
"number_subscriptions": 0,
"phone": "+16175551212",
"processor_type": null,
"reason_payment_method_not_valid": null,
"shopify_customer_id": null,
"status": "INACTIVE",
"stripe_customer_token": "cus_I9bJ...",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38"
}
}Retrieve a customer
Retrieve one customer using the Recharge customer id.
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers/18819267' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token{
"customer": {
"id": 18819267,
"accepts_marketing": true,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"billing_address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"billing_address2": null,
"billing_city": "Los Angeles",
"billing_company": null,
"billing_country": "United States",
"billing_phone": "3103843698",
"billing_province": "California",
"billing_zip": "90404",
"created_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38",
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_charge_processed_at": null,
"first_name": "Mike",
"hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"has_card_error_in_dunning": false,
"has_valid_payment_method": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"number_active_subscriptions": 0,
"number_subscriptions": 0,
"phone": "+16175551212",
"processor_type": null,
"reason_payment_method_not_valid": null,
"shopify_customer_id": null,
"status": "INACTIVE",
"stripe_customer_token": "cus_I9bJ...",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38"
}
}Update a customer
Modify an existing customer to match the specified parameters.
Note: For US citizens parameter billing_zip is required when updating customer’s billing_country parameter
Body Parameters
- accepts_marketingboolean
Indicates whether the
Customergives consent for marketing communications. - emailstring
Email address of the customer.
- billing_address1string
Customer’s billing address 1.
- billing_address2string
An additional field for the customer’s billing address.
- billing_citystring
Customer’s billing city.
- billing_companystring
An additional field for the customer’s company.
- billing_countrystring
Customer’s billing country.
- billing_first_namestring
Customer’s billing first name.
- billing_last_namestring
Customer’s billing last name.
- billing_phonestring
Customers billing phone number.
- billing_provincestring
Customer’s billing province or state name.
- billing_zipstring
Customer’s billing zip or postal code.
- first_namestring
Customer’s first name.
- last_namestring
Customer’s last name.
- phonestring
The customer’s phone number.
- shopify_customer_idinteger
Shopify’s customer id.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers/18819267
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-d '{"billing_address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue"}'{
"customer": {
"id": 18819267,
"accepts_marketing": true,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"billing_address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"billing_address2": null,
"billing_city": "Los Angeles",
"billing_company": null,
"billing_country": "United States",
"billing_phone": "3103843698",
"billing_province": "California",
"billing_zip": "90404",
"created_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38",
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_charge_processed_at": null,
"first_name": "Mike",
"hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"has_card_error_in_dunning": false,
"has_valid_payment_method": false,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"number_active_subscriptions": 0,
"number_subscriptions": 0,
"phone": "+16175551212",
"processor_type": null,
"reason_payment_method_not_valid": null,
"shopify_customer_id": null,
"status": "INACTIVE",
"stripe_customer_token": "cus_I9bJ...",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38"
}
}Delete a customer
Customer deletion will automatically cancel and delete all child Address, Subscription, Onetime, etc. resources of that customer to eliminate orphaned child data.
To delete a certain address without deleting the customer you can use the Delete Address endpoint.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers/18819267
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List customers
Return a list of customers in your store.
## HTTP request examples
GET /customers
GET /customers?email=example@email.com
GET /customers?hash=143806234a9ff87a8d9e
GET /customers?limit=250
GET /customers?page=2
GET /customers?shopify_customer_id=98273498
Query Parameters
- emailstring
Returns the user linked to the email address provided.
- created_at_maxstring
Gets all customers created before this date.
- created_at_minstring
Gets all customers created after this date.
- hashstring
Returns the user linked to the given recharge customer hash.
- idsstring
Filter customers by id. If passing multiple values, must be comma separated. Non-integer values will result in a 422 error
- limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
Number of results.
Default value is 50, maximum is 250. - pagestring*Deprecated
Default: 1
Page to show. Default value is 1.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
- shopify_customer_idstring
Returns the user linked to the given shopify_customer_id.
- statusstring
Returns users with specified status
Values are 'ACTIVE’, and 'INACTIVE’. - updated_at_maxstring
Gets all customers updated before this date.
- updated_at_minstring
Gets all customers updated after this date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d limit=3 -G{
"customers": [
{
"id": 18819267,
"accepts_marketing": true,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": [
{
"utm_campaign": "spring_sale",
"utm_content": "differentiate-content",
"utm_data_source": "website_cookie",
"utm_medium": "email",
"utm_source": "newsletter",
"utm_term": "test-term",
"utm_time_stamp": "2019-12-16T23:57:28.752Z"
}
]
},
"billing_address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"billing_address2": null,
"billing_city": "Los Angeles",
"billing_company": null,
"billing_country": "United States",
"billing_phone": "3103843698",
"billing_province": "California",
"billing_zip": "90404",
"created_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38",
"email": "example_mail@gmail.com",
"first_charge_processed_at": null,
"first_name": "Mike",
"hash": "18819267b1f9095be98f13a8",
"has_card_error_in_dunning": false,
"has_valid_payment_method": true,
"last_name": "Flynn",
"number_active_subscriptions": 0,
"number_subscriptions": 0,
"reason_payment_method_not_valid": null,
"shopify_customer_id": null,
"phone": "+16175551212",
"processor_type": null,
"status": "INACTIVE",
"stripe_customer_token": "cus_I9bJ...",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T08:40:38"
}
]
}Count customers
Retrieve a count of customers.
## HTTP request examples
GET /customers/count
GET /customers/count?created_at_max=2019-11-11
GET /customers/count?created_at_min=2019-11-11
GET /customers/count?created_at_min=2019-11-10&updated_at_max=2019-11-11&status=ACTIVE
GET /customers/count?status=ACTIVE
GET /customers/count?updated_at_max=2019-11-11
GET /customers/count?updated_at_min=2019-11-11
Query Parameters
- created_at_maxstring
Gets count of all customers created before this date.
- created_at_minstring
Gets count of all customers created after this date.
- statusstring
Returns the count of users with the specified status
Values are 'ACTIVE’, and 'INACTIVE’. - updated_at_maxstring
Gets count of all customers updated before this date.
- updated_at_minstring
Gets count of all customers updated after this date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers/count' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"count": 12057
}Payment sources
Retrieve payment sources for customer
This endpoint has been deprecated. Use 2021-01 /payment_methods instead
Query Parameters
- cardholder_namestring
Identifies the owner of the credit card.
- card_brandstring
Identifies the brand of the credit card.
- card_exp_monthstring
The month when the card expires.
- card_exp_yearstring
The year when the card expires.
- card_last4string
The last four digits of the card.
- customer_idstring
Unique customer identifier.
- has_card_error_in_dunningstring
If it has
truevalue, then there was an error in the dunning process. There were no errors in the dunning process if it hasfalsevalue. - payment_typestring*Deprecated
Identifies the payment type. It could have
credit,debit,paypalorapple_payvalues. - processor_namestring
Identifies the payment processor. It could have
stripe,braintreeorauthorizevalue. - statusstring
Identifies the status of the payment method. It could have
activeorfailedvalue. - status_reasonstring
Provides more information on why the payment method is not valid if
statushasfailedvalue.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers/18819267/payment_sources' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"payment_sources": [
{
"billing_address": {
"id": 1,
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"company": null,
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"phone": "3103843698",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90404"
},
"cardholder_name": null,
"card_brand": null,
"card_exp_month": null,
"card_exp_year": null,
"card_last4": null,
"customer_id": 18819267,
"has_card_error_in_dunning": false,
"payment_token": "cus_I9bJ...",
"payment_type": "credit",
"processor_name": "stripe",
"status": "active",
"status_reason": null
}
]
}Discounts
Discounts can be applied to checkout, or can be applied directly to an address. Depending on configuration they allow for single use, or recurring discounts.
Often discounts can be used combination with webhooks, such that when a specific event comes, it can apply a discount dependent on custom business logic.
There are various options that can be utilized for discounts such as minimum price, single use, recurring for a set number of charges, or ongoing. You can also set the date from which time the discount will become applicable begin, and when it can no longer be applied to a new subscription.
The discount object
These fields are deprecated, however they will not be removed from this API version.
applies_to is deprecated. Use applies_to_id and applies_to_resource instead.
Attributes
- idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the customer.
- applies_to_idinteger
Applied to id of the product or collection where the id is the id of the shopify product or the shopify custom collection id.
- applies_to_product_typestring
Possible values: ALL, ONETIME, SUBSCRIPTION
Sets the specific product type the discount applies to.
- channel_settingsobject
A list of channel objects containing information regarding discount behaviors for each.
* can_apply: a boolean to indicate if the discount may be applied using the associated channel (defaults to true for all channels).
If you’re on the SCI Platform, checkout channel will not apply during Shopify checkouts. - codestring
The name of the discount.
- created_atdatetime
The date and time when the discount was created.
- discount_typestring
The type of discount. Either percentage or
fixed_amount. - durationstring
Number of times a discount will be automatically re-applied to a new queued charge after its first usage on a successful charge. Values can be: forever will re-apply unlimited times usage_limit number of times will be set in duration_usage_limit single_use it will not re-apply.
- duration_usage_limitinteger
Specific number of times a discount will be automatically re-applied to a new queued charge after its first usage on a successful charge. *Only used, and is required, when “duration” is set to “usage_limit”.
- ends_atdatetime
The expiration timestamp of the discount. Past this time the
Discountcan no longer be redeemed. Afterends_atthestatusof theDiscountwill go fromactivetodisabled.Recurring discounts applied prior to their
ends_attime will still apply. - first_time_customer_restrictionstring
Discount can be used on checkout for customer that still don’t exist in Recharge database. Default value is null.
- once_per_customerboolean
The discount can only be used once for a given customer checkout or manually applied once on the customer portal (irrespective of which address). Once applied, it will continue being re-applied to each new charge on the address, unless the discount_duration attribute specifies otherwise.
- prerequisite_subtotal_mininteger
The minimum cart subtotal needed for the discount to be applicable.
- starts_atdatetime
The date when the discount becomes active.
When not specified on creation
starts_atwill default tonullwhich translates into no restrictions. - statusstring
The status of the discount. Value can be:
*enableddiscount is active to be applied
*disableddiscount can’t be applied on new purchases. Discount will remain on existing charges to which it has already been applied.
*fully_disableddiscount can no longer be applied. In addition,Discountis removed from every queued charge.disabledandfully_disabledcan both be reverted toenabled. However once aDiscounthas been updated tofully_disabledit will be removed from allChargesit had been applied to. This removal fromChargesis irreversible. - times_usedinteger
Number of times a discount was used by customers at checkout.
- updated_atdatetime
The date and time when the discount was last updated.
- usage_limitinteger
Sets the limit on the number of times a discount can be used by all customers.
- valuestring
The discounted value to be applied.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"discount": {
"id": 3748296,
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ALL",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": false
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": false
}
},
"code": "Discount1",
"created_at": "2018-04-25T14:32:39",
"discount_type": "percentage",
"duration": "usage_limit",
"duration_usage_limit": 10,
"ends_at": "2019-12-15T00:00:00",
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": "2018-05-16T00:00:00",
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2018-05-04T13:33:53",
"usage_limit": 10,
"value": 12
}
}Create a discount
Create a new discount.
With the new ‘prerequisite_subtotal_min’ attribute, you can create discounts that can be applied only if the cart subtotal exceeds a set amount.
Body Parameters
- applies_to_idinteger
Applied to id of the product or collection where the id is the id of the shopify product or the shopify custom collection id.
- applies_to_product_typestring
Possible values: ALL, ONETIME, SUBSCRIPTION
Sets the specific product type the discount applies to.
Possible values: shopify_product, shopify_collection_id
Applied to a specific product or collection.
- channel_settingsobject
A list of channel objects containing information regarding discount behaviors for each.
* can_apply: a boolean to indicate if the discount may be applied using the associated channel (defaults to true for all channels). - codestring* Required
The name of the discount.
- created_atdatetime
The date and time when the discount was created.
- discount_typestring* Required
The type of discount. Either percentage or
fixed_amount. - durationstring* Required
Number of times a discount will be automatically re-applied to a new queued charge after its first usage on a successful charge. Values can be: forever will re-apply unlimited times usage_limit number of times will be set in duration_usage_limit single_use it will not re-apply.
- duration_usage_limitinteger* Required
Specific number of times a discount will be automatically re-applied to a new queued charge after its first usage on a successful charge. *Only used, and is required, when “duration” is set to “usage_limit”.
- ends_atdatetime
The expiration timestamp of the discount. Past this time the
Discountcan no longer be redeemed. Afterends_atthestatusof theDiscountwill go fromactivetodisabled.Recurring discounts applied prior to their
ends_attime will still apply. - first_time_customer_restrictionstring
Possible values: null, customer_must_not_exist_in_recharge
Discount can be used on checkout for customer that still don’t exist in Recharge database. Default value is null.
- once_per_customerboolean
The discount can only be used once for a given customer checkout or manually applied once on the customer portal (irrespective of which address). Once applied, it will continue being re-applied to each new charge on the address, unless the discount_duration attribute specifies otherwise.
- prerequisite_subtotal_mininteger
The minimum cart subtotal needed for the discount to be applicable.
- starts_atdatetime
The date when the discount becomes active.
When not specified on creation
starts_atwill default tonullwhich translates into no restrictions. - statusstring
The status of the discount. Value can be:
*enableddiscount is active to be applied
*disableddiscount can’t be applied on new purchases. Discount will remain on existing charges to which it has already been applied.
*fully_disableddiscount can no longer be applied. In addition,Discountis removed from every queued charge.disabledandfully_disabledcan both be reverted toenabled. However once aDiscounthas been updated tofully_disabledit will be removed from allChargesit had been applied to. This removal fromChargesis irreversible. - usage_limitinteger
Sets the limit on the number of times a discount can be used by all customers.
- valuestring* Required
The discounted value to be applied.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/discounts' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"applies_to_product_type": "ONETIME",
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": false
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": false
}
},
"code": "Discount",
"discount_type": "percentage",
"duration": "usage_limit",
"duration_usage_limit" : 1,
"ends_at" : "2023-12-31",
"starts_at": "2018-05-16",
"status": "enabled",
"usage_limit": 1,
"value": 12
}'{
"discount": {
"id": 3425307,
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ONETIME",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": false
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": false
}
},
"code": "Discount",
"created_at": "2018-04-13T10:00:01",
"discount_type": "percentage",
"duration": "usage_limit",
"duration_usage_limit": 1,
"ends_at": "2023-12-31T00:00:00",
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": "2018-05-16T00:00:00",
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2019-10-16T10:03:38",
"usage_limit": 1,
"value": 12
}
}Retrieve a discount
Retrieve a Recharge Discount
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl'https://api.rechargeapps.com/discounts/1234567' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"discount": {
"id": 3425307,
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ONETIME",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": false
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": false
}
},
"code": "Discount",
"created_at": "2018-04-13T10:00:01",
"discount_type": "percentage",
"duration": "usage_limit",
"duration_usage_limit": 1,
"ends_at": "2023-12-31T00:00:00",
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": "2018-05-16T00:00:00",
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2019-10-16T10:03:38",
"usage_limit": 1,
"value": 12
}
}Update a discount
You can now modify an existing discount to match the specified parameters.
Body Parameters
- channel_settingsstring
A list of channel objects containing information regarding discount behaviors for each.
* can_apply: a boolean to indicate if the discount may be applied using the associated channel (defaults to true for all channels). - ends_atdatetime
The date when the discount will end.
- starts_atdatetime
The date when the discount will start.
- statusstring
The status of the discount. Value can be:
*enableddiscount is active to be applied
*disableddiscount can’t be applied on new purchases. Discount will remain on existing charges to which it has already been applied.
*fully_disableddiscount can no longer be applied. In addition,Discountis removed from every queued charge.disabledandfully_disabledcan both be reverted toenabled. However once aDiscounthas been updated tofully_disabledit will be removed from allChargesit had been applied to. This removal fromChargesis irreversible. - usage_limitinteger
The limit in which a discount can be used.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/discounts/11127406' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"starts_at": "2021-12-06",
"usage_limit" : 10
}'{
"discount": {
"id": 3425307,
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ONETIME",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": false
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": false
}
},
"code": "Discount",
"created_at": "2018-04-13T10:00:01",
"discount_type": "percentage",
"duration": "usage_limit",
"duration_usage_limit": 1,
"ends_at": "2023-12-31T00:00:00",
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": "2018-05-16T00:00:00",
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2019-10-16T10:03:38",
"usage_limit": 1,
"value": 12
}
}Delete a discount
Delete a discount
For safety reasons, to delete a discount you will need to set its status to fully_disabled.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/discounts/12081717' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List discounts
Return a list of discounts in your store.
## HTTP request examples
GET /discounts
GET /discounts?created_at_max=2017-10-01
GET /discounts?created_at_max=2017-10-01
GET /discounts?created_at_min=2017-10-01
GET /discounts?discount_code=Discount
GET /discounts?discount_type=percentage
GET /discounts?updated_at_min=2017-10-01
Query Parameters
- created_at_maxstring
Get all discounts created before a specified date.
- created_at_minstring
Get all discounts created after a specified date.
- discount_codestring
Search for a particular discount code.
- discount_typestring
Type of discount. Value can be
percentageorfixed_amount. - idsstring
Filter discounts by id. If passing multiple values, must be comma separated. Non-integer values will result in a 422 error
- limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
Number of results.
(default:50) (maximum: 250) - pagestring*Deprecated
Page to show.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
- statusstring
Returns all discounts with status
enabledordisabled. - updated_at_maxstring
Get all discounts updated before a specified date.
- updated_at_minstring
Get all discounts updated after a specified date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/discounts' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \ n -d limit=3 -G{
"discounts": [
{
"id": 3748296,
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ALL",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": false
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": false
}
},
"code": "Discount1",
"created_at": "2018-04-25T14:32:39",
"discount_type": "percentage",
"duration": "usage_limit",
"duration_usage_limit": 10,
"ends_at": "2019-12-15T00:00:00",
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": "2018-05-16T00:00:00",
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2018-05-04T13:33:53",
"usage_limit": 10,
"value": 12
}
]
}Count discounts
Receive a count of all discounts.
## HTTP request examples
GET /discounts/count
GET /discounts/count?created_at_min=2019-11-10&created_at_max=2019-11-11
GET /discounts/count?discount_type=percentage
GET /discounts/count?status=enabled
GET /discounts/count?updated_at_min=2019-11-10&updated_at_max=2019-11-11
Query Parameters
- created_at_maxstring
Returns the count of discounts created before a specified date.
- created_at_minstring
Returns the count of discounts created after a specified date.
- discount_typestring
Returns the count of discounts that are of a given type. Value can be percentage,
fixed_amountorshipping. - statusstring
Returns the count of discounts with status of
enabledordisabled. - updated_at_maxstring
Returns the count of discounts updated before a specified date.
- updated_at_minstring
Returns the count of discounts updated after a specified date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/discounts/count' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"count": 12057
}Apply a discount to an address
New endpoint for adding a discount to an existing address.
NOTE: cannot add another discount if the address already has a discount. Also cannot add if an existing queued charge in the address already has a discount.
Body Parameters
- discount_codestring
Code of the discount you want to apply to an address.
- discount_idinteger
Id of the discount you want to apply to an address.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/26031022/apply_discount' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"discount_id": 12406728}'{
"address": {
"id": 26031022,
"address1": "200 Bay St.",
"address2": "",
"cart_attributes": [],
"cart_note": "",
"city": "Toronto",
"company": "",
"country": "Canada",
"created_at": "2019-01-14T22:18:56",
"customer_id": 23124211,
"discount_id": 12406728,
"first_name": "R",
"last_name": "S",
"note_attributes": [],
"original_shipping_lines": [],
"phone": "4163536363",
"province": "Ontario",
"shipping_lines_override": null,
"updated_at": "2019-01-15T11:03:11",
"zip": "M9P 2b6"
}
}Apply a discount to a charge
New endpoint for adding discount to an existing queued charge.
NOTE: You cannot add another discount to an existing queued charge if the charge already has a discount. Also cannot add if the address has an existing discount.
NOTE: You can provide either discount_id or discount_code. If both parameters are passed, the value for discount_id will override the value in discount_code.
If a charge has a discount and it gets updated or a regeneration occurs, the discount will be lost.
Regeneration is a process that refreshes the charge JSON with new data in the case of the subscription/address being updated.
Body Parameters
- discount_codestring
Code of the discount you want to apply to a charge.
- discount_idinteger
Id of the discount you want to apply to a charge.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/charges/105805051/apply_discount' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"discount_code": "test"}'{
"charge": {
"id": 105805051,
"address_id": 22369585,
"billing_address": {
"province": "California",
"city": "Los Angeles",
"first_name": "Mike",
"last_name": "Flynn",
"zip": "90404",
"country": "United States",
"address1": "3030 Nebraska Avenue",
"address2": null,
"company": null,
"phone": "3103843698"
},
"client_details": {
"user_agent": null,
"browser_ip": null
},
"created_at": "2018-11-28T08:51:50",
"customer_hash": null,
"customer_id": 18819267,
"discount_codes": [
{
"amount": "12.00",
"code": "test",
"type": "percentage"
}
],
"email": null,
"first_name": null,
"has_uncommited_changes": false,
"last_name": null,
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 0,
"original_price": "9.00",
"price": "9.00",
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_product_id": "1255175363",
"shopify_variant_id": "3844892483",
"sku": "test",
"subscription_id": 28835632,
"title": "SuperKiwi ONETIME",
"variant_title": "6oz",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
]
}
],
"note": " next order #1 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": null,
"scheduled_at": "2018-11-30T00:00:00",
"shipments_count": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "2298 Primrose Lane",
"address2": "",
"city": "Richland Center",
"company": "Recharge",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "Sherman",
"last_name": "Rivas",
"phone": "6086493200",
"province": "Wisconsin",
"zip": "53581"
},
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": "0.00",
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_order_id": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"sub_total": null,
"subtotal_price": 7.92,
"tags": "Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": 0.38,
"total_discounts": "1.08",
"total_line_items_price": "9.00",
"total_price": "7.92",
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0.38,
"total_weight": 0,
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2019-01-15T11:32:53"
}
}Remove a discount
Remove a discount from a charge or address without destroying the discount.
In most of the cases the discount should be removed from the address. When the discount is removed from the address the discount is also removed from any future charges.
## HTTP request examples
POST /addresses/<address_id>/remove_discount/
POST /charges/<charge_id>/remove_discount/
If the discount is on the parent address, you cannot remove that discount using charge_id. When removing your discount it is preferable to pass the address_id so that the discount stays removed in case the charge is regenerated. Only pass charge_id in edge cases in which there are two or more charges on a parent address and you only want to remove the discount from one charge. If you pass both parameters, it will remove the discount from the address.
Body Parameters
- address_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for address from which you want to remove the discount.
- charge_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier of the charge from which you want to remove the discount.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/26031022/remove_discount' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{}'{
"address": {
"id": 26031022,
"address1": "200 Bay St.",
"address2": "",
"cart_attributes": [],
"cart_note": "a note",
"city": "Toronto",
"company": "",
"country": "Canada",
"created_at": "2019-01-14T22:18:56",
"customer_id": 23124211,
"discount_id": null,
"first_name": "R",
"last_name": "S",
"note_attributes": [],
"original_shipping_lines": [],
"phone": "4163536363",
"province": "Ontario",
"shipping_lines_override": null,
"updated_at": "2019-01-15T11:59:14",
"zip": "M9P 2b6"
}
}Metafields
We now have metafields endpoint on our API!
Metafields feature allows you to add additional information to other resources. They can be used for adding custom fields to objects, and are useful for storing specialized information.
The metafield object
Metafields feature allows you to add additional information to other resources. They can be used for adding custom fields to objects, and are useful for storing specialized information.
Attributes
- idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the metafield.
- created_atdatetime
The date and time when the metafield was created.
- descriptionstring
Description of the metafield.
- keystring
The name of the metafield.
- namespacestring
A category or container that differentiates your metadata from other metafields.
- owner_idstring
Unique numeric identifier of the owner resource.
- owner_resourcestring
The owner of the resource can be one of the following values:
address,store,customer,subscription,order,charge. There may be more objects added in the future. - updated_atdatetime
The date and time when the metafield was last updated.
- valuestring
The content of the metafield.
- value_typestring
The type of the value parameter.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"metafield": {
"id": 33,
"created_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"description": "customer_phone_number",
"key": "phone_number",
"namespace": "personal_info",
"owner_id": 18301938,
"owner_resource": "customer",
"updated_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"value": "3103103101",
"value_type": "integer"
}
}Create a metafield
Creates metafield for specific object.
Note:There is a limit of 50 metafields per owner_id.
Body Parameters
- descriptionstring
Description of the metafield.
- keystring* Required
The name of the metafield.
- namespacestring* Required
A category or container that differentiates your metadata from other metafields.
- owner_idinteger* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the owner resource.
- owner_resourcestring* Required
The owner of the resource can be one of the following values:
address,store,customer,subscription,order,charge. There may be more objects added in the future. - valuestring* Required
The content of the metafield.
- value_typestring* Required
The type of the value parameter. Valid values are
"string","json_string"and"integer"
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/metafields' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"metafield": {
"description": "customer_phone_number",
"key": "phone_number",
"namespace": "personal_info",
"owner_resource": "customer",
"owner_id": 18301938,
"value_type": "integer",
"value": "3103103101"
}
}'{
"metafield": {
"id": 33,
"created_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"description": "customer_phone_number",
"key": "phone_number",
"namespace": "personal_info",
"owner_id": 18301938,
"owner_resource": "customer",
"updated_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"value": "3103103101",
"value_type": "integer"
}
}Retrieve a metafield
Retrieves a single metafield based on specified id.
## HTTP request examples
GET /metafields/<metafield_id>
In addition to that, you can retrieve them by “subscription_id” by using:
GET /metafields?owner_resource=subscription&owner_id=<subscription_id>
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/metafields/33' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"metafield": {
"id": 33,
"created_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"description": "customer_phone_number",
"key": "phone_number",
"namespace": "personal_info",
"owner_id": 18301938,
"owner_resource": "customer",
"updated_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"value": "3103103101",
"value_type": "integer"
}
}Update a metafield
Updates metafield based on specified owner resource.
Body Parameters
- descriptionstring
Description of the metafield.
- owner_idstring
Unique numeric identifier of the resource.
- owner_resourcestring
The owner of the resource can be one of the following values:
address,store,customer,subscription,order,charge. There may be more objects added in the future. - valuestring
The content of the metafield.
- value_typestring
The type of the value parameter. Valid values are
"string","json_string"and"integer"
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/metafields/33' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"metafield": {
"description": "phone_number_of_customer",
"owner_id": 18293088,
"owner_resource": "customer",
"value": "0333103133",
"value_type": "integer"
}
}'{
"metafield": {
"id": 33,
"created_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"description": "customer_phone_number",
"key": "phone_number",
"namespace": "personal_info",
"owner_id": 18301938,
"owner_resource": "customer",
"updated_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"value": "3103103101",
"value_type": "integer"
}
}Delete a metafield
Delete a metafield
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/metafields/6' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List metafields
Retrieves a list of metafields.
## HTTP request examples
GET /metafields?owner_resource=<owner_resource>
GET /metafields?owner_resource=subscription&owner_id=<subscription_id>
GET /metafields?owner_resource=customer&owner_id=<customer_id>
GET /metafields?owner_resource=store&owner_id=<store_id>
When getting metafields, you must specify owner_resource in the URL. It can be address, store, customer, subscription, order, charge
You can list metafields that are created for all subscription objects using:
GET /metafields?owner_resource=subscription - **owner_id** in the response will be the ID of the subscription.
Metafields are filterable by any of the following parameters:
Query Parameters
- limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
Amount of results.
(default:50) (maximum: 250). - namespacestring
A category or container that differentiates your metadata from other metafields.
- owner_idstring
Unique numeric identifier of the owner resource.
- owner_resourcestring
The owner of the resource can be one of the following values:
address,store,customer,subscription,order,charge. There may be more objects added in the future. - pagestring*Deprecated
Page to show.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/metafields?owner_resource=store' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d limit=3 -G{
"metafields": [
{
"id": 33,
"created_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"description": "customer_phone_number",
"key": "phone_number",
"namespace": "personal_info",
"owner_id": 18301938,
"owner_resource": "customer",
"updated_at": "2018-11-07T14:00:10",
"value": "3103103101",
"value_type": "integer"
},
{
"id": 15,
"created_at": "2018-11-05T12:59:30",
"description": "desc lorem ipsum",
"key": "marjan",
"namespace": "nmsp2c",
"owner_id": 17868054,
"owner_resource": "customer",
"updated_at": "2018-11-05T15:48:42",
"value": "5",
"value_type": "integer"
},
{
"id": 9,
"created_at": "2018-11-05T12:47:27",
"description": "desc lorem ipsum",
"key": "marjan",
"namespace": "nmspc",
"owner_id": 17868054,
"owner_resource": "customer",
"updated_at": "2018-11-05T12:47:27",
"value": "5",
"value_type": "integer"
}
]
}Count metafields
Retrieves a number of metafields for some specific query parameter.
## HTTP request examples
GET /metafields/count?owner_resource=<owner_resource>
When getting metafields, you must specify owner_resource in the URL. It can be address, store, customer, subscription, order, charge
Query Parameters
- namespacestring
A category or container that differentiates your metadata from other metafields.
- owner_idstring
Unique numeric identifier of the owner resource.
- owner_resourcestring
The owner of the resource can be one of the following values:
address,store,customer,subscription,order,charge. There may be more objects added in the future.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/metafields/count?owner_resource=store' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"count": 3
}Notifications
The Customer Notifications API is used to dispatch email notifications to customers within Recharge. The API uses your configured Recharge email templates, and will dispatch an email to the address associated with the indicated customer_id. Some email templates require variable values, which are sent through the Customer Notifications API via the template_vars attribute. See below examples for all available template types.
Currently, the Customer Notifications API can be used to dispatch Get Account Access, and Upcoming Charge emails. Support for additional email templates and message types will be added in the future. To view your email template configurations, see the Notifications Settings section in your Recharge Merchant Portal.
Send email notification
Sends an upcoming charge email to the customer with the customer_id indicated in the route. To view the upcoming charge email template, visit the Notifications section in your Recharge Merchant Admin Portal.
Body Parameters
- typeinteger* Required
Identifies the type of the notifications. Value can be email only.
- template_typestring* Required
Possible values: upcoming_charge, get_account_access
Identifies the type of the email notifications. To send an “Upcoming Charge” email, set value to upcoming_charge
- template_varsobject
An object containing the necessary template variables for this email template type.
Show object attributes
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/customers/18819267/notifications' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"type": "email",
"template_type": "upcoming_charge",
"template_vars":{
"address_id":1234567890,
"charge_id":9876543210
}
}'{}Onetimes
Onetimes represent non-recurring line items on a QUEUED Charge.
The onetime object
Attributes
- idinteger
One Time subscription id.
- address_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the address the One Time Purchase is associated with (cannot be used with
next_charge_scheduled_at) - add_to_next_chargeboolean
Boolean used to automatically add One Time Purchase to the next scheduled charge associated with the indicated address record.
- created_atstring
The time the One Time Product was first created.
- customer_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the customer the One Time Purchase is tied to.
- next_charge_scheduled_atstring
Date of the One Time Purchase execution.
- priceinteger
The price of the item before discounts, taxes, or shipping have been applied.
- product_titlestring
The name of the product in a shop’s catalog.
- propertiesarray
The list of line item objects.
- quantityinteger
The number of items on the subscription.
- recharge_product_idinteger
Unique number identifier of the product in Recharge.
- shopify_product_idinteger
Unique number identifier of the product in Shopify.
- shopify_variant_idinteger
Unique number identifier of the product variant in Shopify.
- skustring
A unique identifier of the item in the fulfillment.
- statusstring
The status of the One Time Purchase.
- updated_atstring
The time the One Time Purchase was last updated.
- variant_titlestring
The name of the variant in a shop’s catalog.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"onetime": {
"id": 16909886,
"address_id": 21317826,
"created_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2018-12-17T00:00:00",
"price": null,
"product_title": "SuperKiwi ONETIME",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 518672,
"shopify_product_id": 1255175363,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844892483,
"sku": null,
"status": "ONETIME",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"variant_title": "6oz"
}
}Create a onetime
Create a new Onetime.
Body Parameters
- add_to_next_chargeboolean
Boolean used to automatically add One Time Purchase to the next scheduled charge associated with the indicated address record.
- next_charge_scheduled_atdatetime* Required
This will set the charge date of a new One Time Purchase (cannot be used with
add_to_next_charge). - priceinteger
The price of the product.
- product_titlestring
The name of the product.
- propertiesstring
List of properties.
- quantityinteger* Required
The quantity of the product.
- shopify_product_idinteger* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the product in Shopify.
- shopify_variant_idinteger* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the product variant in Shopify.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/21317826/onetimes' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2021-12-17",
"price": 9,
"product_title": "SuperKiwi ONETIME",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
},
{
"name": "size",
"value": "medium"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844892483
}'{
"onetime": {
"id": 16909886,
"address_id": 21317826,
"created_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2021-12-17T00:00:00",
"price": null,
"product_title": "SuperKiwi ONETIME",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 518672,
"shopify_product_id": 1255175363,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844892483,
"sku": null,
"status": "ONETIME",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"variant_title": "6oz"
}
}Retrieve a onetime
Retrieve a Onetime.
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/onetimes/16909886' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"onetime": {
"id": 16909886,
"address_id": 21317826,
"created_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2021-12-17T00:00:00",
"price": null,
"product_title": "SuperKiwi ONETIME",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
},
{
"name": "size",
"value": "medium"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 518676,
"shopify_product_id": 1255175363,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844892483,
"sku": null,
"status": "ONETIME",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"variant_title": "6oz"
}
}Update a onetime
Update an existing One Time Product.
Body Parameters
- next_charge_scheduled_atboolean
This will set the charge date of a new One Time Purchase (cannot be used with
add_to_next_charge). - priceinteger
The price of the product.
- product_titlestring
The name of the product.
- propertiesstring
List of properties.
- quantityinteger
The quantity of the product.
- shopify_variant_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier of the product variant in Shopify.
- skustring
A unique alphanumeric identifier of the item in the fulfillment.
- variant_titlestring
The name of the product variant.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -x PUT https://api.rechargeapps.com/onetimes/16909886
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' -d '{"quantity": 1}'{
"onetime": {
"id": 16909886,
"address_id": 21317826,
"created_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2021-12-17T00:00:00",
"price": null,
"product_title": "SuperKiwi ONETIME",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
},
{
"name": "size",
"value": "medium"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 518676,
"shopify_product_id": 1255175363,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844892483,
"sku": null,
"status": "ONETIME",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"variant_title": "6oz"
}
}Delete a onetime
Delete a Onetime.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE https://api.rechargeapps.com/onetimes/16665185
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List onetimes
Returns a list of all One Time products from store.
Query Parameters
- address_idstring
Return the onetimes linked to the given address_id.
- created_at_maxstring
Return the onetimes created before the given date.
- created_at_minstring
Return the onetimes created after the given date.
- customer_idstring
Return the onetimes linked to the given Recharge customer id.
- limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
The number of results. Default is 50, maximum is 250.
- pagestring*Deprecated
Default: 1
The page to show. Default is 1.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
- shopify_customer_idstring
Return the onetimes linked to the given Shopify customer id.
- updated_at_maxstring
Return the onetimes updated before the given date.
- updated_at_minstring
Return the onetimes updated after the given date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/onetimes' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d limit=3 -G{
"onetimes": [
{
"id": 16909886,
"address_id": 21317826,
"created_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"customer_id": 18819267,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2018-12-17T00:00:00",
"price": null,
"product_title": "SuperKiwi ONETIME",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
},
{
"name": "size",
"value": "medium"
}
],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 518676,
"shopify_product_id": 1255175363,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844892483,
"sku": null,
"status": "ONETIME",
"updated_at": "2018-11-14T11:20:05",
"variant_title": "6oz"
}
]
}Orders
An order is created after a charge is successfully processed. The order contains all the same json data as the charge. In case of a prepaid order creation, the order will be queued for a particular date and submitted on that date to shopify.
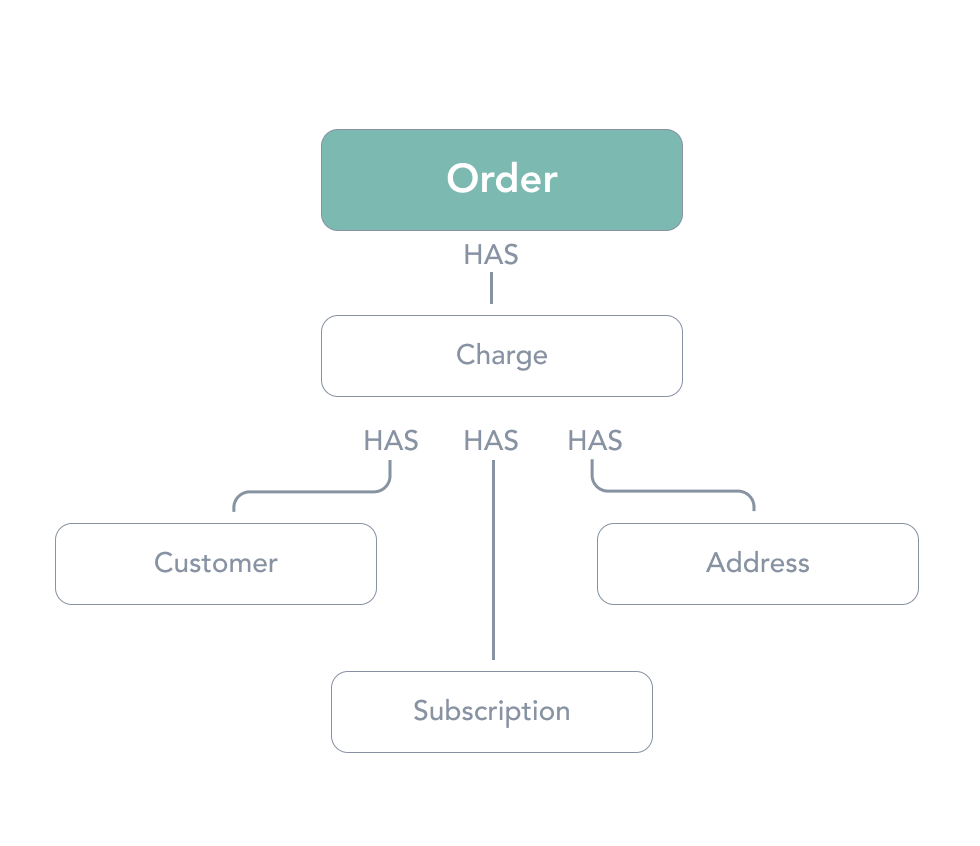
The order object
These fields are deprecated, however they will not be removed from this API version.
product_title is deprecated. Use title instead.
shipping_date is deprecated. Use scheduled_at instead.
shopify_id is deprecated. Use shopify_order_id instead.
address_is_active is deprecated. Please ignore, not an applicable field.
Attributes
- idinteger
The unique numeric identifier for the order.
- billing_addressobject
The billing address at the time the order was created. See addresses for detailed address information.
Show object attributes - currencystring
The currency of the payment used to create the order.
- customerobject
Object that contains information about the customer.
Show object attributes - emailstring
The email address of the customer.
- first_namestring
The first name of the customer.
- is_prepaidboolean
The order that has been paid for a pre-determined number of months. 0=No, 1=Yes.
- last_namestring
The last name of the customer.
- line_itemsarray
A list of line item objects, each one containing information about an item in the order.
Show object attributes - payment_processorstring
The type of payment the processor has chosen.
- processed_atstring
The date when the order was submitted.
- scheduled_atdatetime
The date when the order will be shipped.
- shipping_addressobject
The shipping address where the order will be shipped. See addresses for detailed address information.
Show object attributes - shopify_cart_tokenstring
Unique cart token generated by Shopify when an item is added to the cart.
- shopify_customer_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier within Shopify for the customer.
- shopify_order_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier within Shopify for the order.
- shopify_order_numberinteger
The unique order number within Shopify.
- statusstring
The status of creating the order within Shopify.
- transaction_idstring
The unique alphanumeric identifier of the transaction.
- total_priceinteger
The sum of all of the prices of the items in the order with taxes and discounts included (must be positive).
- total_dutiesstring
The total cost of duties for the order.
- typestring
Shows if order was made thorough checkout or if it’s a recurring charge. Inputs: “CHECKOUT” or “RECURRING”.
Error related attributes
- errorstring
String describing the reason for the error state.
More Attributes
- address_idinteger
The id of the customer shipping address that this order is tied to.
- address_is_activeboolean
Tells if address is currently active. 0=No, 1=Yes.
Deprecated. Not an applicable field. - charge_idinteger
The unique numeric identifier of the charge.
- created_atdatetime
The date when the order was created.
- customer_idinteger
The unique numeric identifier of the customer.
- shipping_datedatetime
The date when the order will be processed.
Use scheduled_at instead. - shopify_idstring
Unique numeric identifier within Shopify for the order.
Deprecated, use shopify_order_id instead. - updated_atdatetime
The date when the order was last updated.
{
"order": {
"id": 70071255,
"address_id": 4029306,
"address_is_active": 1,
"billing_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"charge_id": 97376832,
"charge_status": "SUCCESS",
"created_at": "2018-11-08T08:08:09",
"currency": "USD",
"customer": {
"accepts_marketing": true,
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": null,
"send_email_welcome": false,
"verified_email": true
},
"customer_id": 4203912,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"error": "",
"first_name": "mike",
"hash": "42039120ee0e6cfa5c97805",
"is_prepaid": 1,
"last_name": "flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"external_inventory_policy": "decrement_obeying_policy",
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_large.jpeg",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_medium.jpeg",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2.jpeg",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_small.jpeg"
},
"original_price": "17.00",
"price": "17.00",
"product_title": "Milk",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
},
{
"name": "size",
"value": "medium"
}
],
"quantity": 4,
"shopify_product_id": 1255183683,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844924611,
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 26375706,
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"title": "Milk",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "shopifyCartToken_littledata:45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff GAClientId:1215763073.1492751771 - next order #3 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": [],
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"processed_at": null,
"scheduled_at": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipped_date": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"shipping_date": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": 0,
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_cart_token": "45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff",
"shopify_customer_id": "6454896021",
"shopify_id": null,
"shopify_order_id": null,
"shopify_order_number": null,
"status": "CANCELLED",
"subtotal_price": 0,
"tags": "Prepaid, Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": 0,
"total_duties": 0,
"total_line_items_price": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 18144,
"transaction_id": "ch_1DUDEtJ2zqHvZRd1EQHjapRD",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-12-20T13:25:52"
}
}Retrieve an order
Retrieve one order using the Recharge order id.
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders/70071255' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"order": {
"id": 70071255,
"address_id": 4029306,
"address_is_active": 1,
"billing_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"charge_id": 97376832,
"charge_status": "SUCCESS",
"created_at": "2018-11-08T08:08:09",
"currency": "USD",
"customer": {
"accepts_marketing": true,
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": null,
"send_email_welcome": false,
"verified_email": true
},
"customer_id": 4203912,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"error": "",
"first_name": "mike",
"hash": "42039120ee0e6cfa5c97805",
"is_prepaid": 1,
"last_name": "flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_large.jpeg",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_medium.jpeg",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2.jpeg",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_small.jpeg"
},
"original_price": "17.00",
"price": "17.00",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
},
{
"name": "size",
"value": "medium"
}
],
"quantity": 4,
"shopify_product_id": 1255183683,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844924611,
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 26375706,
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "shopifyCartToken_littledata:45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff GAClientId:1215763073.1492751771 - next order #3 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": [],
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"processed_at": null,
"scheduled_at": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipped_date": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"shipping_date": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": 0,
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_cart_token": "45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff",
"shopify_customer_id": "6454896021",
"shopify_id": null,
"shopify_order_id": null,
"shopify_order_number": null,
"status": "CANCELLED",
"subtotal_price": 0,
"tags": "Prepaid, Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": 0,
"total_duties": 0,
"total_line_items_price": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 18144,
"transaction_id": "ch_1DUDEtJ2zqHvZRd1EQHjapRD",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-12-20T13:25:52"
}
}Update an order
Updating existing order is now available for pre-paid subscriptions.
Body Parameters
- billing_addressobject
The key values you would like to update:
address1 optional
province required
address2 optional
city optional
company optional
country optional
first_name optional
last_name optional
phone optional
zip optional - shipping_addressobject
The key values you would like to update:
address1 optional
province required
address2 optional
city optional
company optional
country optional
first_name optional
last_name optional
phone optional
zip optional - customerobject
The key values related with customer you would like to update:
first_name optional
last_name required
email optional
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders/70071255' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"billing_address": {
"city": "Los Angeles",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"zip": "90025"
}
}'{
"order": {
"id": 70071255,
"address_id": 4029306,
"address_is_active": 1,
"billing_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"charge_id": 97376832,
"charge_status": "SUCCESS",
"created_at": "2018-11-08T08:08:09",
"currency": "USD",
"customer": {
"accepts_marketing": true,
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": null,
"send_email_welcome": false,
"verified_email": true
},
"customer_id": 4203912,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"error": "",
"first_name": "mike",
"hash": "42039120ee0e6cfa5c97805",
"is_prepaid": 1,
"last_name": "flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"external_inventory_policy": "decrement_obeying_policy",
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_large.jpeg",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_medium.jpeg",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2.jpeg",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/milk2_small.jpeg"
},
"original_price": "17.00",
"price": "17.00",
"product_title": "Milk",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
},
{
"name": "size",
"value": "medium"
}
],
"quantity": 4,
"shopify_product_id": 1255183683,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844924611,
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 26375706,
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"title": "Milk",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "shopifyCartToken_littledata:45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff GAClientId:1215763073.1492751771 - next order #3 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": [],
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"processed_at": null,
"scheduled_at": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipped_date": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"shipping_date": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipping_lines": [
{
"code": "Standard Shipping",
"price": 0,
"title": "Standard Shipping"
}
],
"shopify_cart_token": "45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff",
"shopify_customer_id": "6454896021",
"shopify_id": null,
"shopify_order_id": null,
"shopify_order_number": null,
"status": "CANCELLED",
"subtotal_price": 0,
"tags": "Prepaid, Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": 0,
"total_duties": 0,
"total_line_items_price": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 18144,
"transaction_id": "ch_1DUDEtJ2zqHvZRd1EQHjapRD",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-12-20T13:25:52"
}
}Delete an order
You can delete a scheduled order.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders/70071255' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List orders
Returns a list of orders.
## HTTP request examples
GET /orders
GET /orders?customer_id=123
GET /orders?address_id=4587216
GET /orders?charge_id=45678542
GET /orders?created_at_min=2016-05-18&created_at_max=2016-06-18
Query Parameters
- address_idstring
Filter orders by address.
GET /orders/?address_id=123will return all orders for the givenaddress_id - charge_idstring
Filter orders by charge.
GET /orders/?charge_id=123will return all orders for the givencharge_id - created_at_maxstring
Show orders created before the given date.
- created_at_minstring
Show orders created after the given date.
- customer_idstring
Filter orders by customer.
GET /orders/?customer_id=123will return all orders for the givencustomer_id - idsstring
Filter orders by id. If passing multiple values, must be comma separated. Non-integer values will result in a 422 error
- limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
The number of results. Default is 50, maximum is 250.
- pagestring*Deprecated
Default: 1
The page to show. Default is 1.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
- scheduled_at_maxstring
Show orders scheduled before the given date.
- scheduled_at_minstring
Show orders scheduled after the given date.
- shipping_datestring
The date when the order will be processed and sent to Shopify.
Deprecated, use scheduled_at instead. - shopify_order_idstring
Filter orders by shopify_order_id.
- has_external_orderstring
Filter orders with/without shopify_order_id (external_order_id). Default value is null
- statusstring
Filter orders by status. Available status: “SUCCESS”, “QUEUED”, “ERROR”, “REFUNDED”, “SKIPPED”.
- subscription_idstring
Filter orders by subscriptions.
GET /orders/?subscription_id=123will return all orders for the givensubscription_id - updated_at_maxstring
Show orders updated before the given date.
- updated_at_minstring
Show orders updated after the given date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d limit=3 -G{
"orders": [
{
"id": 70071255,
"address_id": 4029306,
"address_is_active": 1,
"billing_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"charge_id": 97376832,
"charge_status": "SUCCESS",
"created_at": "2018-11-08T08:08:09",
"currency": "USD",
"customer": {
"accepts_marketing": true,
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": null,
"send_email_welcome": false,
"verified_email": true
},
"customer_id": 4203912,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"hash": "42039120ee0e6cfa5c97805",
"is_prepaid": 1,
"last_name": "flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 0,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "0.00",
"price": "0.00",
"product_title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 4,
"shopify_product_id": 1255183683,
"shopify_variant_id": 32720763846,
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 26375706,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "shopifyCartToken_littledata:45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff GAClientId:1215763073.1492751771 - next order #3 - Subscription Recurring Order",
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"processed_at": null,
"scheduled_at": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipped_date": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"shipping_date": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipping_lines": [],
"shopify_cart_token": "45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff",
"shopify_customer_id": "6454896021",
"shopify_id": null,
"shopify_order_id": null,
"shopify_order_number": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"subtotal_price": 0,
"tags": "Prepaid, Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": 0,
"total_duties": 0,
"total_line_items_price": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 0,
"transaction_id": "ch_1DUDEtJ2zqHvZRd1EQHjapRD",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-11-09T10:07:52"
}
]
}Count orders
Retrieve a count of all orders.
## HTTP request examples
GET /orders/count
GET /orders/count
GET /orders/count?address_id=123123
GET /orders/count?charge_id=123123
GET /orders/count?created_at_min=2015-01-01&created_at_max=2019-02-02
GET /orders/count?customer_id=123123
GET /orders/count?scheduled_at_min=2016-01-01&scheduled_at_max=2019-02-02
GET /orders/count?shopify_customer_id=123123123
GET /orders/count?subscription_id=123123
GET /orders/count?status=queued
Query Parameters
- address_idstring
Filter orders by address.
GET /orders/?address_id=123will return all orders for the givenaddress_id - charge_idstring
Filter orders by charge.
GET /orders/?charge_id=123will return all orders for the givencharge_id - created_at_maxstring
Show orders created before the given date.
- created_at_minstring
Show orders created after the given date.
- customer_idstring
Filter orders by customer.
GET /orders/?customer_id=123will return all orders for the givencustomer_id - scheduled_at_maxstring
Show orders scheduled before the given date.
- scheduled_at_minstring
Show orders scheduled after the given date.
- shopify_customer_idstring
Return the count of orders by shopify_customer_id.
- statusstring
Filter orders by status. Available status: “SUCCESS”, “QUEUED”, “ERROR”, “REFUNDED”, “SKIPPED”.
- subscription_idstring
Filter orders by subscriptions.
GET /orders/?subscription_id=123will return all orders for the givensubscription_id - updated_at_maxstring
Show orders updated before the given date.
- updated_at_minstring
Show orders updated after the given date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders/count' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"count": 38667
}Change an order date
Modify the shipping date of the order.
Body Parameters
- scheduled_atdatetime* Required
New shipping date in ISO 8601 format.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders/7271806/change_date' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"scheduled_at": "2018-07-01T00:00:00"}'{
"order": {
"id": 70071255,
"address_id": 4029306,
"address_is_active": 1,
"billing_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"charge_id": 97376832,
"charge_status": "SUCCESS",
"currency": "USD",
"customer": {
"accepts_marketing": true,
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": null,
"send_email_welcome": false,
"verified_email": true
},
"created_at": "2018-11-08T08:08:09",
"customer_id": 4203912,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"hash": "42039120ee0e6cfa5c97805",
"is_prepaid": 1,
"last_name": "flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 0,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "0.00",
"price": "0.00",
"product_title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 4,
"shopify_product_id": 1255183683,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844924611,
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 26375706,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "next order #3",
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"processed_at": null,
"scheduled_at": "2018-07-01T00:00:00",
"shipped_date": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"shipping_date": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipping_lines": [],
"shopify_cart_token": "45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff",
"shopify_customer_id": "6454896021",
"shopify_id": null,
"shopify_order_id": null,
"shopify_order_number": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"subtotal_price": 0,
"tags": "Prepaid, Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": 0,
"total_duties": 0,
"total_line_items_price": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 0,
"transaction_id": "ch_1DUDEtJ2zqHvZRd1EQHjapRD",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-06-09T10:07:52"
}
}Change an order variant
Modify the shopify product variant of the order.
Body Parameters
- new_shopify_variant_idinteger* Required
Unique numeric identifier of new shopify product variant.
- shopify_variant_idstring* Required
Unique numeric identifier of existing shopify product variant.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders/1234/update_shopify_variant/454545' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"new_shopify_variant_id": "32720763846"}'{
"order": {
"id": 70071255,
"address_id": 4029306,
"address_is_active": 1,
"billing_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"charge_id": 97376832,
"charge_status": "SUCCESS",
"currency": "USD",
"customer": {
"accepts_marketing": true,
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": null,
"send_email_welcome": false,
"verified_email": true
},
"created_at": "2018-11-08T08:08:09",
"customer_id": 4203912,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"hash": "42039120ee0e6cfa5c97805",
"is_prepaid": 1,
"last_name": "flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 0,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "0.00",
"price": "0.00",
"product_title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 4,
"shopify_product_id": 1255183683,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844924611,
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 26375706,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "next order #3",
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"processed_at": null,
"scheduled_at": "2018-07-01T00:00:00",
"shipped_date": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"shipping_date": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipping_lines": [],
"shopify_cart_token": "45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff",
"shopify_customer_id": "6454896021",
"shopify_id": null,
"shopify_order_id": null,
"shopify_order_number": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"subtotal_price": 0,
"tags": "Prepaid, Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": 0,
"total_duties": 0,
"total_line_items_price": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 0,
"transaction_id": "ch_1DUDEtJ2zqHvZRd1EQHjapRD",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-06-09T10:07:52"
}
}Clone an order
You may add additional Orders onto a success Charge if it has existing prepaid Orders by cloning an existing Order.
Body Parameters
- scheduled_atdatetime* Required
Date in future when this order will be sent.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders/clone_order_on_success_charge/70071255/charge/100714428' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"scheduled_at": "2022-11-16"}'{
"order": {
"id": 70071255,
"address_id": 4029306,
"address_is_active": 1,
"billing_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"charge_id": 97376832,
"charge_status": "SUCCESS",
"currency": "USD",
"customer": {
"accepts_marketing": true,
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": null,
"send_email_welcome": false,
"verified_email": true
},
"created_at": "2018-11-08T08:08:09",
"customer_id": 4203912,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"hash": "42039120ee0e6cfa5c97805",
"is_prepaid": 1,
"last_name": "flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 0,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "0.00",
"price": "0.00",
"product_title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 4,
"shopify_product_id": 1255183683,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844924611,
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 26375706,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "next order #3",
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"processed_at": null,
"scheduled_at": "2018-07-01T00:00:00",
"shipped_date": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"shipping_date": "2022-11-16T00:00:00",
"shipping_lines": [],
"shopify_cart_token": "45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff",
"shopify_customer_id": "6454896021",
"shopify_id": null,
"shopify_order_id": null,
"shopify_order_number": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"subtotal_price": 0,
"tags": "Prepaid, Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": 0,
"total_duties": 0,
"total_line_items_price": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 0,
"transaction_id": "ch_1DUDEtJ2zqHvZRd1EQHjapRD",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2018-06-09T10:07:52"
}
}Delay an order
Delay a prepaid Order by one interval
The id must be for the next queued Order for a prepaid Subscription. The Order will be delayed by one interval, and all subsequent Orders and Charges will be shifted by the same amount.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X POST 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/orders/70071255/delay' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"order": {
"id": 70071255,
"address_id": 4029306,
"address_is_active": 1,
"billing_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"charge_id": 97376832,
"charge_status": "QUEUED",
"created_at": "2022-02-04T18:19:52",
"currency": "USD",
"customer": {
"accepts_marketing": true,
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": null,
"send_email_welcome": false,
"verified_email": true
},
"customer_id": 4203912,
"discount_codes": [],
"email": "examlpe@email.com",
"first_name": "mike",
"hash": "42039120ee0e6cfa5c97805",
"is_prepaid": 1,
"last_name": "flynn",
"line_items": [
{
"grams": 0,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_large.png",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__medium.png",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee_.png",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/.../Sumatra_Coffee__small.png"
},
"original_price": "0.00",
"price": "0.00",
"product_title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"properties": [
{
"name": "grind",
"value": "drip"
}
],
"quantity": 4,
"shopify_product_id": 1255183683,
"shopify_variant_id": 3844924611,
"sku": "MILK-1",
"subscription_id": 26375706,
"title": "Sumatra Coffee Dark",
"variant_title": "Milk - a / b"
}
],
"note": "next order #3",
"note_attributes": null,
"payment_processor": "stripe",
"processed_at": null,
"scheduled_at": "2023-03-07T00:00:00",
"shipped_date": null,
"shipping_address": {
"address1": "1933 Manning",
"address2": "204",
"city": "los angeles",
"company": "bootstrap",
"country": "United States",
"first_name": "mike",
"last_name": "flynn",
"phone": "3103103101",
"province": "California",
"zip": "90025"
},
"shipping_date": "2023-03-07T00:00:00",
"shipping_lines": [],
"shopify_cart_token": "45af6dbe140d8dc1a9b7821ae256cfff",
"shopify_customer_id": "6454896021",
"shopify_id": null,
"shopify_order_id": null,
"shopify_order_number": null,
"status": "QUEUED",
"subtotal_price": 0,
"tags": "Prepaid, Subscription, Subscription Recurring Order",
"tax_lines": [
{
"price": "0.950",
"rate": 0.0725,
"title": "CA State Tax"
},
{
"price": "0.335",
"rate": 0.0225,
"title": "Los Angeles County Tax"
}
],
"total_discounts": 0,
"total_duties": 0,
"total_line_items_price": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"total_refunds": null,
"total_tax": 0,
"total_weight": 0,
"transaction_id": "ch_1DUDEtJ2zqHvZRd1EQHjapRD",
"type": "RECURRING",
"updated_at": "2023-01-17T11:36:08"
}
}Products
The subscription settings associated to a remote catalog product
Deprecated: The Products endpoints in the 2021-01 API version are deprecated. Please use the Plans endpoints in the 2021-11 API to manage frequencies, subscription discounts, and related settings for Products.
The product object
product_id is scheduled for deprecation. Use the shopify_product_id instead. number_charges_until_expiration is scheduled for deprecation. Use expire_after_specific_number_of_charges instead.
Attributes
- idinteger
Unique numeric identifier of the product in Recharge.
- charge_interval_frequencyinteger
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each charge.
- collection_idinteger*Deprecated
Unique numeric identifier for the ruleset created in Recharge.
- created_atdatetime
Date and time when ruleset was created.
- cutoff_day_of_monthinteger
Number of day in month on which customer will be charged. Cut-off windows create an interval between the day a customer goes through Recharge checkout to purchase a new subscription and when you charge that customer again for their recurring order.
Min value: 1
Max value: 31 - cutoff_day_of_weekinteger
Number of day in week on which customer will be charged. Cut-off windows create an interval between the day a customer goes through Recharge checkout to purchase a new subscription and when you charge that customer again for their recurring order.
Min value: 0 (Monday)
Max value: 6 (Sunday) - discount_amountinteger
Discount amount applied on the ruleset.
- discount_typestring
Type of discount.
- expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesinteger
Number of charges until subscription expires.
- handlestring
A human-friendly unique string for the product automatically generated from Shopify.
- imagesobject
Images of product in Shopify.
- modifiable_propertiesarray
List of modifiable line item properties
Example:["box-edition", "christmas-special"] - number_charges_until_expirationinteger
Number of charges until subscription expires.
Will be deprecated, use expire_after_specific_number_of_charges instead. - order_day_of_monthinteger
The set day of the month order is created. Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the month when the order is created. This is only applicable to subscriptions with order_interval_unit = “month”.
- order_day_of_weekinteger
The set day of the week order is created. Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the week order is created. This is only applicable to subscriptions with order_interval_unit = “week”. Value of 0 equals to Monday, 1 to Tuesday etc.
- order_interval_frequency_optionsstring
List of order interval frequency options that customer can choose from. For example, order_interval_unit=month and order_interval_frequency_option for 3 would be an order every 3 months. Max value: 999
- order_interval_unitstring
The frequency with which a subscription should have the order created with. Valid values are “day”, “week”, and “month”.
- product_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier of the product in Shopify.
Will be deprecated, use shopify_product_id instead. - shopify_product_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier of the product in Shopify.
- storefront_purchase_optionsstring
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_only"- Your product(s) will only be offered as a recurring subscription item.
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_and_onetime"- Your product(s) will have the option of being purchased as a one-time item or as a recurring subscription item. - titlestring
Product title retrieved from Shopify.
- updated_atdatetime
Date and time when ruleset is updated.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"product": {
"id": 1327844,
"created_at": "2019-11-07T11:36:19",
"discount_amount": 10,
"discount_type": "percentage",
"handle": null,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_large.jpg",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_medium.jpg",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt.jpg",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_small.jpg"
},
"product_id": 4354268856408,
"shopify_product_id": 4354268856408,
"subscription_defaults": {
"charge_interval_frequency": 1,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"modifiable_properties": [
"name",
"quantity",
"size",
"color"
],
"number_charges_until_expiration": null,
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency_options": [
"1",
"6",
"12"
],
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_only"
},
"title": "T-shirt",
"updated_at": "2019-11-07T11:36:19"
}
}Create a product
Create product for offer.
Body Parameters
- charge_interval_frequencyinteger
Max: 999
• The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each charge.
- collection_idinteger*Deprecated
• Unique numeric identifier for the ruleset created in Recharge.
- cutoff_day_of_monthstring
• Number of day in month on which customer will be charged.
• If it is set then “shipping_interval_unit” must be equal to “month”.
• Min value: 1
• Max value: 31. - cutoff_day_of_weekstring
•Number of day in week on which customer will be charge.
•If it is set then “order_interval_unit” must be equal to “week”.
• Min value: 0 (Monday)
• Max value: 6 (Sunday) - discount_amountstring
• Discount amount applied on subscription product.
- discount_typestring
• Type of discount on subscription product.
• Valid option is only “percentage”. - expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesstring
• Number of charges until subscription expires.
- modifiable_propertiesstring
• List of modifiable line item properties
• Example: [“box-edition”, “christmas-special”] - order_day_of_monthstring
• The set day of the month order is created.
• Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the month when the order is created.
• Only applicable when order_interval_unit = “month”. - order_day_of_weekstring
• The set day of the week order is created.
• Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the week order is created.
• Only applicable when order_interval_unit = “week”.
• Value of 0 equals Monday, 1 equals Tuesday, etc. - order_interval_frequency_optionsstring
• List of order interval frequency options that customer can choose from.
- order_interval_unitstring
• The frequency with which a subscription should have orders created.
- shopify_product_idinteger* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the product in Shopify.
- storefront_purchase_optionsstring
• Valid options are “subscription_only” or “subscription_and_onetime”.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/products' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"discount_amount": 10.0,
"discount_type": "percentage",
"shopify_product_id": 4354268856408,
"subscription_defaults": {
"charge_interval_frequency": 1,
"modifiable_properties": [
"color"
"name",
"quantity",
"size",
],
"order_interval_frequency_options": [
"1"
],
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_only"
}
}'{
"product": {
"id": 1327844,
"created_at": "2019-11-07T11:36:19",
"discount_amount": 10,
"discount_type": "percentage",
"handle": null,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_large.jpg",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_medium.jpg",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt.jpg",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_small.jpg"
},
"product_id": 4354268856408,
"shopify_product_id": 4354268856408,
"subscription_defaults": {
"charge_interval_frequency": 1,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"modifiable_properties": [
"color",
"name",
"quantity",
"size"
],
"number_charges_until_expiration": null,
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency_options": [
"1",
"6",
"12"
],
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_only"
},
"title": "T-shirt",
"updated_at": "2019-11-07T11:36:19"
}
}Retrieve a product
Retrieves product from store.
Query Parameters
- charge_interval_frequencystring
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each charge.
- created_atstring
Date and time when ruleset is created.
- cutoff_day_of_monthstring
Number of day in month on which customer will be charged. Cut-off windows create an interval between the day a customer goes through Recharge checkout to purchase a new subscription and when you charge that customer again for their recurring order. Min value: 1 Max value: 31
- cutoff_day_of_weekstring
Number of day in week on which customer will be charged. Cut-off windows create an interval between the day a customer goes through Recharge checkout to purchase a new subscription and when you charge that customer again for their recurring order.
Min value: 0 (Monday)
Max value: 6 (Sunday) - discount_amountstring
Discount amount applied on ruleset.
- discount_typestring
Type of discount.
- expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesstring
Number of charges until subscription expires.
- handlestring
A human-friendly unique string for the product automatically generated from Shopify.
- imagesstring
array of dictionary object
“images”: {…}
Images of product in Shopify. - modifiable_propertiesstring
List of modifiable line item properties
Example:["box-edition", "christmas-special"] - number_charges_until_expirationstring
Number of charges until subscription expires.
Will be deprecated, use expire_after_specific_number_of_charges instead. - order_day_of_monthstring
The set day of the month order is created. Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the month when the order is created. This is only applicable to subscriptions with order_interval_unit = “month”.
- order_day_of_weekstring
The set day of the week order is created. Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the week order is created. This is only applicable to subscriptions with order_interval_unit = “week”. Value of 0 equals to Monday, 1 to Tuesday etc.
- order_interval_frequencystring
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each order. For example, order_interval_unit=month and order_interval_frequency=3, indicate order every 3 months. Max value: 999
- order_interval_frequency_optionsstring
List of order interval frequency options that customer can choose from.
- order_interval_unitstring
The frequency with which a subscription should have order created. Valid values are “day”, “week”, and “month”.
- product_idstring
Unique numeric identifier of the product in Shopify.
Will be deprecated, use shopify_product_id instead. - shopify_product_idinteger
-Your product(s) will only be offered as a recurring subscription item.
-Your product(s) will have the option of being purchased as a one-time item or as a recurring subscription item. - storefront_purchase_optionsstring
Unique numeric identifier of collection.
- titlestring
Product title retrieved from Shopify.
- updated_atstring
Date and time when ruleset is updated.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/products/1327844' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"product": {
"id": 1327844,
"created_at": "2019-11-07T11:36:19",
"discount_amount": 10,
"discount_type": "percentage",
"handle": null,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_large.jpg",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_medium.jpg",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt.jpg",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_small.jpg"
},
"product_id": 4354268856408,
"shopify_product_id": 4354268856408,
"subscription_defaults": {
"charge_interval_frequency": 1,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"modifiable_properties": [
"color",
"name",
"quantity",
"size"
],
"number_charges_until_expiration": null,
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency_options": [
"1",
"6",
"12"
],
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_only"
},
"title": "T-shirt",
"updated_at": "2019-11-07T11:36:19"
}
}Update a product
Update an existing product.
Body Parameters
- charge_interval_frequencyinteger
• The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each charge.
• Min value: 1
• Max value: 999 - collection_idinteger*Deprecated
• Unique numeric identifier for the ruleset created in Recharge.
- cutoff_day_of_monthstring
• Number of day in month on which customer will be charged.
• If it is set then “shipping_interval_unit” must be equal to “month”.
• Min value: 1
• Max value: 31 - cutoff_day_of_weekstring
•Number of day in week on which customer will be charge.
•If it is set then “order_interval_unit” must be equal to “week”.
• Min value: 0 (Monday)
• Max value: 6 (Sunday) - discount_amountstring
• Discount amount applied on subscription product.
- discount_typestring
• Type of discount on subscription product.
• Valid option is only “percentage”. - expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesstring
• Number of charges until subscription expires.
- modifiable_propertiesstring
• List of modifiable line item properties
• Example: [“box-edition”, “christmas-special”] - order_day_of_monthstring
• The set day of the month order is created.
• Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the month when the order is created.
• Only applicable when order_interval_unit = “month”. - order_day_of_weekstring
• The set day of the week order is created.
• Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the week order is created.
• Only applicable when order_interval_unit = “week”.
• Value of 0 equals Monday, 1 equals Tuesday, etc. - order_interval_frequency_optionsstring*Deprecated
• List of order interval frequency options that customer can choose from.
• Must be list of integers or integers that are individual strings.
• Each integer/string must be greater than 0 and less than 999. - order_interval_unitstring
• The frequency with which a subscription should have orders created.
- shopify_product_idinteger* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the product in Shopify.
- storefront_purchase_optionsstring
Possible values: subscription_only, subscription_and_onetime
Buying options.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/products/1327844' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"discount_amount": 15.0,
"subscription_defaults": {
"charge_interval_frequency": 4,
"order_interval_frequency_options": [
"1",
"6"
]
}
}'{
"product": {
"id": 1327844,
"collection_id": null,
"created_at": "2019-11-07T11:36:19",
"discount_amount": 10,
"discount_type": "percentage",
"handle": null,
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_large.jpg",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_medium.jpg",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt.jpg",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/t_shirt_small.jpg"
},
"product_id": 4354268856408,
"shopify_product_id": 4354268856408,
"subscription_defaults": {
"charge_interval_frequency": 1,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"modifiable_properties": [
"color",
"name",
"quantity",
"size"
],
"number_charges_until_expiration": null,
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency_options": [
"1",
"6",
"12"
],
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_only"
},
"title": "T-shirt",
"updated_at": "2019-11-07T11:36:19"
}
}Delete a product
Delete product from store.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/products/509780' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List products
Lists products from store.
## HTTP request examples
GET /products
GET /products?ids=<id>,<id>,<id>,<id>,<id>
GET /products?shopify_product_ids=<shopify_product_id>,<shopify_product_id>,<shopify_product_id>
Query Parameters
- idstring
Unique numeric identifier of product in Recharge.
- limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
The amount of results. Maximum is 250, default is 50.
- shopify_product_idinteger
- pagestring*Deprecated
Default: 1
The page to show. Default value is 1.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl https://api.rechargeapps.com/products
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"products": [
{
"id": 645083,
"created_at": "2018-01-31T10:32:29",
"discount_amount": 35,
"discount_type": "percentage",
"handle": "red-energy",
"images": {
"large": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/metal-drinks-can-red-8217566_large.jpeg",
"medium": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/metal-drinks-can-red-8217566_medium.jpeg",
"original": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/metal-drinks-can-red-8217566.jpeg",
"small": "https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0683/1951/products/metal-drinks-can-red-8217566_small.jpeg"
},
"product_id": 1255175363,
"shopify_product_id": 1255175363,
"subscription_defaults": {
"charge_interval_frequency": 3,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": null,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"modifiable_properties": [
"color",
"name",
"quantity",
"size"
],
"number_charges_until_expiration": null,
"order_day_of_month": 0,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": 1,
"order_interval_frequency_options": [
"1"
],
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_and_onetime"
},
"title": "<b>Red Energy<br></b>",
"updated_at": "2019-11-03T13:04:36"
},
{
"id": 607491,
"created_at": "2017-12-18T11:43:45",
"discount_amount": 0,
"discount_type": "percentage",
"handle": "banana-meri",
"images": {
"large": "",
"medium": "",
"original": "",
"small": ""
},
"product_id": 89293422613,
"shopify_product_id": 89293422613,
"subscription_defaults": {
"charge_interval_frequency": 4,
"cutoff_day_of_month": null,
"cutoff_day_of_week": 6,
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"modifiable_properties": [
"color",
"name",
"quantity",
"size"
],
"number_charges_until_expiration": null,
"order_day_of_month": 0,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": 2,
"order_interval_frequency_options": [
"2"
],
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"storefront_purchase_options": "subscription_only"
},
"title": "Banana Meri",
"updated_at": "2019-11-03T13:04:36"
},
{}
]
}Count products
Retrieve a count of all products.
## HTTP request examples
GET /products/count
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/products/count' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"count": 500
}Shop
The shop endpoint includes basic info about your Recharge store setup.
Retrieve a shop
Retrieve store using the Recharge API.
Shop properties.
These fields are deprecated, however they will not be removed from this API version. email is deprecated. Use shop_email instead.
Query Parameters
- idinteger
Unique number identifier of the store.
- created_atdatetime
Date and time when the store is created.
- currencystring
Currency of the store.
- domainstring
Global domain name of the store.
- emailstring
Store-owner e-mail
Will be deprecated, use shop_email instead. - iana_timezonestring
Iana database timezone format.
- my_shopify_domainstring
Store domain name in Shopify.
- namestring
Name of the store.
- shop_phonestring
Phone number of the store owner.
- shop_emailstring
E-mail address of the store owner.
- timezonestring
Timezone of the store.
- updated_atdatetime
Date and time when the store was updated.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/shop' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"shop": {
"checkout_logo_url": ""
},
"store": {
"id": 1100010523,
"checkout_platform": "recharge",
"created_at": "Thu, 10 Jan 2018 08:40:45 GMT",
"currency": "USD",
"domain": "example-store.com",
"email": "example@gmail.com",
"enabled_presentment_currencies": [
"USD"
],
"enabled_presentment_currencies_symbols": [
{
"currency": "USD",
"location": "before",
"suffix": "",
"symbol": "$"
}
],
"disabled_currencies_historical": [],
"iana_timezone": "America/New_York",
"my_shopify_domain": "example-store.myshopify.com",
"name": "Example Store",
"shop_email": "example@gmail.com",
"shop_phone": "9075553333",
"timezone": "(GMT-05:00) Eastern Time (US & Canada)",
"updated_at": "Wed, 10 Mar 2019 05:17:23 GMT"
}
}Shipping countries
Retrieve shipping countries where items can be shipped.
## HTTP request examples
GET /shop/shipping_countries
Query Parameters
- idinteger
Unique identifier of country for store in Recharge.
- codestring
It represents country code per ISO standards.
- country_idinteger
Unique identifier of country.
- namestring
Country name.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/shop/shipping_countries' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"shipping_countries": [
{
"id": 156172,
"code": "US",
"country_id": 227,
"name": "United States",
"provinces": [
{
"id": 2138,
"code": "AL",
"name": "Alabama"
},
{
"id": 2133,
"code": "AK",
"name": "Alaska"
},
{
"id": 2115,
"code": "AS",
"name": "American Samoa"
}
]
},
{
"id": 172110,
"code": "CA",
"country_id": 37,
"name": "Canada",
"provinces": [
{
"id": 1947,
"code": "AB",
"name": "Alberta"
},
{
"id": 1941,
"code": "BC",
"name": "British Columbia"
},
{
"id": 1948,
"code": "MB",
"name": "Manitoba"
}
]
},
{
"id": 156151,
"code": "IE",
"country_id": 103,
"name": "Ireland",
"provinces": []
}
]
}Subscriptions
Subscriptions are individual items a customer receives on a recurring basis.
A subscription is a product added to an address.
If store owner wants to sell multiple products as one subscription on 1 address it can be done by creating a product in Shopify that consists of multiple products e.g. 3 types of vegetables in the box, set of different shirts, etc. This multiple products appear on the store as 1 product, therefore it can be sold in a single subscription to 1 or more addresses. 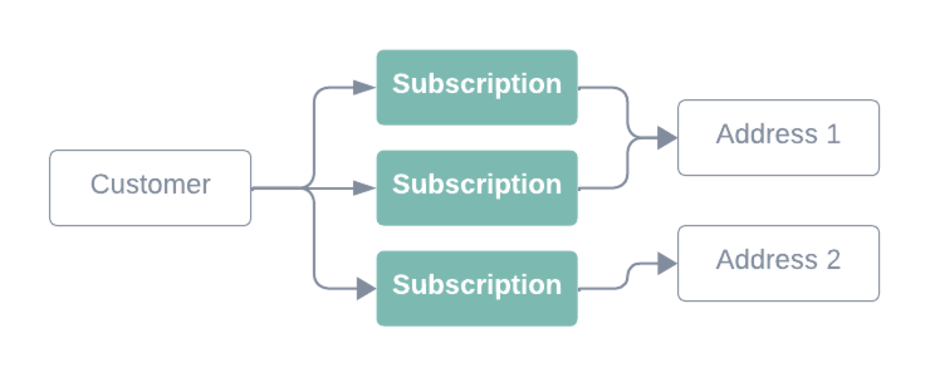
The subscription object
These fields are deprecated, however they will not be removed from this API version.
product_title is deprecated. Use title instead.
shipping_date is deprecated. Use scheduled_at instead.
shopify_id is deprecated. Use shopify_order_id instead.
address_is_active is deprecated. Please ignore, not an applicable field.
Attributes
- idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the subscription.
- address_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the address the subscription is associated with.
- cancellation_reasonstring
Reason provided for cancellation.
- cancellation_reason_commentstring
Additional comment for cancellation.
- cancelled_atstring
The time the subscription was cancelled.
- charge_interval_frequencystring
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each charge. For example, order_interval_unit=month and charge_interval_frequency=3, indicate charge every 3 months. Charges must use the same unit types as orders. Max value: 1000
- created_atstring
The time the subscription was created.
- customer_idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the customer the subscription is tied to.
- emailstring
The email address of the customer.
- expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesinteger
Set the number of charges until subscription expires.
- has_queued_chargesboolean
Retrieves 1 if there is queued charge. Otherwise, retrieves 0.
- is_prepaidboolean
Value is set to True if it is a prepaid item.
- is_skippableboolean
Value is set to True if it is not a prepaid item
- is_swappableboolean
Value is set to True if it is not a prepaid item and if in Customer portal settings swap is allowed for customers.
- max_retries_reachedboolean
Retrieves 1 if charge has an error max retries reached. Otherwise, retrieves 0.
- next_charge_scheduled_atstring
Date of the next charge for the subscription.
- order_day_of_monthinteger
The set day of the month order is created. Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the month when the order is created. This is only applicable to subscriptions with order_interval_unit = “month”.
- order_day_of_weekinteger
The set day of the week order is created. Default is that there isn’t a strict day of the week order is created. This is only applicable to subscriptions with order_interval_unit = “week”. Value of 0 equals to Monday, 1 to Tuesday etc.
- order_interval_frequencystring
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each order. For example, order_interval_unit=month and order_interval_frequency=3, indicate order every 3 months. Max value: 1000
- order_interval_unitstring
The frequency which a subscription should have the order created with. Valid values are “day”, “week”, and “month”.
- priceinteger
The price of the item before discounts, taxes, or shipping have been applied.
- product_titlestring
The name of the product in a shop’s catalog.
- propertiesstring
A list of line item objects, each one containing information about the subscription. Custom key-value pairs can be installed here, they will appear on the connected queued charge and after it is processed on the order itself.
- quantityinteger
The number of items in the subscription.
- recharge_product_idinteger
Unique number identifier of the product in Recharge.
- shopify_product_idinteger
Unique number identifier of the product in Shopify.
- shopify_variant_idinteger
Unique number identifier of the product variant in Shopify.
- skustring
A unique identifier of the item in the fulfillment. In cases where SKU is blank, it will be dynamically pulled whenever it is used.
- sku_overrideboolean
Flag that is automatically updated to true when SKU is passed on create or update. When sku_override is true, the sku on the subscription will be used to generate charges and orders. When sku_override is false, Recharge will dynamically fetch the SKU from the corresponding shopify variant.
- statusstring
The status of the subscription. Valid values:
• ACTIVE - The subscription is active.
• CANCELLED - The subscription has been cancelled.
• EXPIRED - The subscription has expired. This occurs when the maximum number of charges for a product has been reached. - variant_titlestring
The name of the variant in a shop’s catalog.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"subscription": {
"id": 89559201,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": true,
"is_skippable": false,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "15",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "White"
},
{
"name": "Package Material",
"value": "Paper"
}
],
"quantity": 3,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284380775,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
}Create a subscription
When creating a subscription via API, “order_interval_frequency” and “charge_interval_frequency” values do not necessarily need to match the values set in the respective ruleset. The product, however, does need to be a part of a ruleset in order to be added to a subscription.
Body Parameters
- address_idinteger* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the customer’s address.
- charge_interval_frequencyinteger* Required
The number of units, specified in order_interval_unit, between each charge.
- customer_idstring
Unique numeric identifier of the customer.
- expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesstring
The number of charges until the subscription expires.
- next_charge_scheduled_atstring* Required
This will set the first charge date of a new subscription.
- order_day_of_monthstring
This is populated when order_interval_unit has value “month”. Default value is 0.
- order_day_of_weekstring
This is populated when order_interval_unit has value “week”.
- order_interval_frequencystring* Required
The number of units, specified in order_interval_unit, between each order.
- order_interval_unitstring* Required
The frequency which a subscription should have the order created with. Valid values are “day”, “week”, and “month”.
- pricestring
The price of the product.
- propertiesstring
The list of line item objects.
- product_titlestring
The name of the product.
- quantitystring* Required
The quantity of the product
- shopify_product_idstring* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the product id in Shopify.
- shopify_variant_idstring* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the product variant id in Shopify.
- statusstring
Default: ACTIVE
Default is set to “ACTIVE”.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"address_id": 48563471,
"charge_interval_frequency":"30",
"next_charge_scheduled_at":"2020-07-15",
"order_interval_frequency":"15",
"order_interval_unit":"day",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "Yellow"
},
{
"name": "Bottle Material",
"value": "Glass"
}
]
"shopify_variant_id":32165284380775,
"shopify_product_id":4546063663207
"quantity":3
}'{
"subscription": {
"id": 89559201,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": true,
"is_skippable": false,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "15",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "White"
},
{
"name": "Package Material",
"value": "Paper"
}
],
"quantity": 3,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284380775,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
}Retrieve a subscription
Retrieve a subscription using the Recharge subscription id.
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/27363808' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"subscription": {
"id": 89559201,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": true,
"is_skippable": false,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "15",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "White"
},
{
"name": "Package Material",
"value": "Paper"
}
],
"quantity": 3,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284380775,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
}Update a subscription
Update an existing subscription.
Updating parameters like frequency, charge_interval_frequency, order_interval_frequency, order_interval_unit will affect our algorithm to automatically recalculate the next charge date (next_charge_scheduled_at). If you want to change the next charge date (next_charge_scheduled_at) we recommend you to update these parameters first.
When updating subscription “status” attribute from “CANCELLED” to “ACTIVE”, following attributes will be set to null: “cancelled_at”, “cancellation_reason” and “cancellation_reason_comments”
When updating order_interval_unit OR order_interval_frequency OR charge_interval_frequency all three parameters are required
Query Parameters
- force_updateboolean
If set to
True, updates will also be applied toCANCELLEDsubscriptions. IfnullorFalse, onlyACTIVEsubscriptions will be updated.
More Parameters
Body Parameters
- charge_interval_frequencystring* Required
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each charge. Required when updating order_interval_unit.
WARNING: This update will remove skipped and manually changed charges. - commit_updateboolean
Controls whether the
QUEUEDcharges linked to the subscription should be regenerated upon subscription update. By default the flag is set totruewhich means the charges get regenerated for everyPUT. Having the flag set tofalsewill delay charge regeneration 5 seconds so you can run multiple calls to perform the changes and you’ll be able to receive responses much faster since your app won’t wait between requests and responses for every charge regeneration to complete. - expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesstring
The number of charges until subscription expires.
- order_day_of_monthstring
The day of the month the order is created on.
WARNING: this update will remove skips and manually changed charges. - order_day_of_weekstring
The day of the week the order is created on.
WARNING: this update will remove skips and manually changed charges. - order_interval_frequencystring* Required
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each order. Required when updating order_interval_unit.
WARNING: This update will remove skipped and manually changed charges. - order_interval_unitstring* Required
The frequency which a subscription should have the order created with. Valid values are “day”, “week”, and “month”.
WARNING: This update will remove skipped and manually changed charges. - overridestring
Advanced usage only When used, this allows for updating a prepaid subscription variant, which otherwise is not allowed because of the complexity of results. Use with caution.
- pricestring
The price of the item before discounts, taxes, or shipping has been applied.
- product_titlestring
The name of the product.
- propertiesstring
List of properties.
- quantitystring
The number of items in the subscription.
- shopify_variant_idstring
[Swap Product (NEW)][1]
Unique number identifier of the product variant in Shopify. - skustring
A unique identifier of the item in the fulfillment.
- sku_overridestring
Flag is automatically updated to true when SKU is passed on create or update. When sku_override is true, the sku on the subscription will be used to generate charges and orders. When sku_override is false, Recharge will dynamically fetch the sku from the corresponding shopify variant.
- use_shopify_variant_defaultsboolean
Flag instructing to pull the
price,sku,variant_title, andproduct_titlefrom the provided Shopify variant.You need to pass the
variant_idand set this attribute totruein the request for the flag to work. - variant_titlestring
The name of the product variant.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/27363808' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"quantity": 4}'{
"subscription": {
"id": 89559201,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": true,
"is_skippable": false,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "15",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "White"
},
{
"name": "Package Material",
"value": "Paper"
}
],
"quantity": 3,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284380775,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
}Delete a subscription
We now have a feature for deleting a subscription.
Body Parameters
- send_emailboolean
When your store setting indicates that cancellation emails should be sent, this value determines if the email should be sent for the specified subscription cancellation. If set to 1, cancellation emails will be sent for the specified subscription cancellations. If set to 0, cancellation emails will not be sent.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE -H 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/89559201' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List subscriptions
Returns a list of all your subscriptions.
## HTTP request examples
GET /subscriptions
GET /subscriptions?created_at_min=2018-10-10&created_at_max=2019-10-16
GET /subscriptions?customer_id=<customer_id>
Query Parameters
- address_idstring
Return the subscriptions linked to the given address id.
- created_at_maxstring
Return the subscriptions created before the given date.
- created_at_minstring
Return the subscriptions created after the given date.
- customer_idstring
Return the subscriptions linked to the given Recharge customer id.
- idsstring
Comma-separated list of subscription ids to filter
- include_onetimesstring
(beta-feature)
When set as true the response will contain onetimes and subscriptions that meet the given search criteria. Onetimes will be sent as an array with the key “onetimes” and subscriptions will be sent as an array with the key “subscriptions”. If no onetimes or subscriptions meet the search criteria, the corresponding array will be empty. Requires one of the following search parameters:
* address_id
* customer_id
* shopify_customer_id
Note: this feature requires a beta flag that must be enabled by Recharge. - limitstring
Default: 50
Max: 250
The number of results. Default value is 50 and maximum is 250.
- pagestring*Deprecated
Default: 1
The page to show. Default value is 1.
Page-based pagination has been deprecated but still available to use for pages up to a 100. If you need data past this point, use cursor pagination.
- shopify_customer_idstring
Return the subscriptions linked to the given Shopify customer id.
- shopify_variant_idstring
Return the subscriptions linked to the given Shopify product variant id.
- statusstring
Return the subscriptions with specified status. Status can have the following values:
• ACTIVE - The subscription is active.
• CANCELLED - The subscription has been cancelled.
• EXPIRED - The subscription has expired. This occurs when the maximum number of charges for a product has been reached. - updated_at_maxstring
Return the subscriptions updated before the given date.
- updated_at_minstring
Return the subscriptions updated after the given date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-d limit=3 -Gcurl https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' -d limit=3 -G
curl -X DELETE -H https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/89559201 -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"subscriptions": [
{
"id": 89560571,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:01",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": false,
"is_skippable": true,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-16T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "30",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 7,
"product_title": "Orange Juice Auto renew",
"properties": [],
"quantity": 2,
"recharge_product_id": 1463299,
"shopify_product_id": 4578081833063,
"shopify_variant_id": 32309455192167,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:01",
"variant_title": "Squeezed"
}
]
}Count subscriptions
Returns the count of subscriptions.
## HTTP request examples
GET /subscriptions/count
GET /subscriptions/count?customer_id=123123123
GET /subscriptions/count?address_id=123123123
GET /subscriptions/count?status=ACTIVE
GET /subscriptions/count?shopify_customer_id=123123123123
GET /subscriptions/count?shopify_variant_id=123123123123
GET /subscriptions/count?updated_at_min=2019-11-10-&updated_at_max=2019-11-11
GET /subscriptions/count?created_at_min=2019-11-10-&updated_at_max=2019-11-11
Query Parameters
- address_idstring
Return the count of subscriptions linked to the given address id.
- created_at_maxstring
Return the count of subscriptions created before the given date.
- created_at_minstring
Return the count of subscriptions created after the given date.
- customer_idstring
Return the count of subscriptions linked to the given customer id.
- shopify_customer_idstring
Return the count of subscriptions linked to the given Shopify customer id.
- shopify_variant_idstring
Return the count of subscriptions that have the provided shopify_variant_id
- statusstring
Return the count of subscriptions with specified status. Status can have the following values:
• ACTIVE - The subscription is active.
• CANCELLED - The subscription has been cancelled.
• EXPIRED - The subscription has been expired. This occurs when the maximum number of charges for a product has been reached. - updated_at_maxstring
Return the count of subscriptions updated before the given date.
- updated_at_minstring
Return the count of subscriptions updated after the given date.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/count' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"count": 120457
}Change a subscription next charge date
Update an existing subscription’s next charge date.
Note: if there are two active subscriptions with the same address_id, and you update their next_charge_date parameters to match, their charges will get merged into a new charge with a new id
Body Parameters
- datestring* Required
The next charge date desired.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/27363808/set_next_charge_date' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"date": "2021-08-05"}'{
"subscription": {
"id": 89559201,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": true,
"is_skippable": false,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "15",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "White"
},
{
"name": "Package Material",
"value": "Paper"
}
],
"quantity": 3,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284380775,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
}Change a subscription address
Update an existing subscription’s address.
Body Parameters
- address_idstring* Required
Unique id of the address that need to be associated with subscription.
- next_charge_scheduled_atstring
Date and time when next charge need to be scheduled.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/27363808/change_address' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"address_id": 23397943}'{
"subscription": {
"id": 89559201,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": true,
"is_skippable": false,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "15",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "White"
},
{
"name": "Package Material",
"value": "Paper"
}
],
"quantity": 3,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284380775,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
}Cancel a subscription
Cancel an active subscription.
An involuntary subscription cancelled due to max retries reached will trigger the charge/max_retries_reached webhook.
Body Parameters
- cancellation_reasonstring* Required
Reason for subscription cancellation.
- cancellation_reason_commentsstring
Cancellation reason comment. Maximum length is 1024 characters.
- send_emailstring
If set to
false, subscription cancelled email will not be sent to customer and store owner. Note: even if set to True, there are some conditions where an email will not be sent. They are: inactive subscription_cancellation email template, customer or subscription was created on the same day, subscription is for a membership, email already sent for this subscription in the last 24 hours, customer has other active subscriptions or onetimes
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/27363808/cancel' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"cancellation_reason": "other reason"}'{
"subscription": {
"id": 89559201,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": true,
"is_skippable": false,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "15",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "White"
},
{
"name": "Package Material",
"value": "Paper"
}
],
"quantity": 3,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284380775,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
}Activate a subscription
Activate a cancelled subscription.
When activating subscription, following attributes will be set to null: “cancelled_at”, “cancellation_reason” and “cancellation_reason_comments”
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/subscriptions/27363808/activate' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your api token' \
-d '{}'{
"subscription": {
"id": 89559201,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"is_prepaid": true,
"is_skippable": false,
"is_swappable": false,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "15",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [
{
"name": "Colour",
"value": "White"
},
{
"name": "Package Material",
"value": "Paper"
}
],
"quantity": 3,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284380775,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:30:51",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
}Bulk create subscriptions
Bulk create new subscriptions.
There is a limit of 20 subscriptions per request.
Body Parameters
- charge_interval_frequencystring* Required
The number of units, specified in order_interval_unit, between each charge.
- customer_idstring
Unique numeric identifier of the customer.
- expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesstring
The number of charges until subscription expires.
- next_charge_scheduled_atstring* Required
This will set the first charge date of a new subscription.
- order_day_of_monthstring
This is populated when order_interval_unit has value “month”. Default value is 0.
- order_day_of_weekstring
This is populated when order_interval_unit has value “week”.
- order_interval_frequencystring
The number of units, specified in order_interval_unit, between each order.
- order_interval_unitstring* Required
The frequency which a subscription should have the order created with. Valid values are “day”, “week”, and “month”.
- pricestring
The price of the product.
- product_titlestring
The name of the product.
- propertiesstring
The list of line item objects.
- quantitystring* Required
The quantity of the product.
- shopify_variant_idstring* Required
Unique numeric identifier of the product variant in Shopify.
- statusstring
Default: ACTIVE
Default is set to “ACTIVE”.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/42420080/subscriptions-bulk' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"subscriptions":
[
{
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-16",
"order_interval_frequency": "30",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"quantity": 2,
"shopify_variant_id": 32309455192167
},
{
"charge_interval_frequency": "6",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": 4,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-13",
"order_interval_frequency": "1",
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_variant_id": 32309455224935
},
{
"charge_interval_frequency": "4",
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-08-01",
"order_interval_frequency": "4",
"order_interval_unit": "week",
"quantity": 1,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284479079
}
]
}'{
"subscriptions": [
{
"id": 89560571,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-16T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "30",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 7,
"product_title": "Orange Juice Auto renew",
"properties": [],
"quantity": 2,
"recharge_product_id": 1463299,
"shopify_product_id": 4578081833063,
"shopify_variant_id": 32309455192167,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"variant_title": "Squeezed"
},
{
"id": 89560572,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "6",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": 4,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-13T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "1",
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"price": 7,
"product_title": "Orange Juice Auto renew",
"properties": [],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 1463299,
"shopify_product_id": 4578081833063,
"shopify_variant_id": 32309455224935,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"variant_title": "Can"
},
{
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "4",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"id": 89560574,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-08-01T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "4",
"order_interval_unit": "week",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284479079,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
]
}Bulk update subscriptions
Bulk update existing subscriptions
There is a limit of 20 subscriptions per request.
Updating parameters like frequency, charge_interval_frequency, order_interval_frequency, and order_interval_unit will affect our algorithm to automatically recalculate the next charge date (next_charge_scheduled_at). If you want to change the next charge date (next_charge_scheduled_at) we recommend you update these parameters first.
When updating the subscription status attribute from CANCELLED to ACTIVE, the following attributes will be set to null: cancelled_at, cancellation_reason, and cancellation_reason_comments.
When updating order_interval_unit OR order_interval_frequency OR charge_interval_frequency, all three parameters are required.
Body Parameters
- idstring* Required
Unique identifier of subscription.
- address_idstring
Can be used to change the address of the subscriptions.
- cancellation_reasonstring
Used to provide cancellation reason when cancelling subscriptions.
- cancellation_reason_commentsstring
If
cancellation_reasonis provided, this attribute can be used to provide additional cancellation reason comments. Maximum length is 1024 characters. - charge_interval_frequencystring* Required
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each charge. Required when updating order_interval_unit.
WARNING: This update will remove skipped and manually changed charges. - expire_after_specific_number_of_chargesstring
The number of charges until the subscription expires.
- force_updateboolean
If set to
True, updates will also be applied toCANCELLEDsubscriptions. IfnullorFalse, onlyACTIVEsubscriptions will be updated. - next_charge_scheduled_atstring* Required
Can be used to change the date of the next queued charge (must be current or future date).
- order_day_of_monthstring
The day of the month order is created.
WARNING: this update will remove skips and manually changed charges. - order_day_of_weekstring
The day of the week order is created.
WARNING: this update will remove skips and manually changed charges. - order_interval_frequencystring
The number of units (specified in order_interval_unit) between each order. Required when updating order_interval_unit.
WARNING: This update will remove skipped and manually changed charges. - order_interval_unitstring* Required
The frequency which a subscription should have the order created with. Valid values are “day”, “week”, and “month”.
WARNING: This update will remove skipped and manually changed charges. - pricestring
The price of the item before discounts, taxes, or shipping has been applied.
- product_titlestring
The name of the product.
- propertiesstring
List of properties.
- quantitystring
The number of items in subscription.
- send_emailstring
If set to false, subscription cancelled email will not be sent to customer and store owner.
- shopify_variant_idstring
[Swap Product (NEW)][1]
Unique number identifier of the product variant in Shopify. - skustring
A unique identifier of the item in the fulfillment.
- sku_overridestring
Flag is automatically updated to true when SKU is passed on create or update. When sku_override is true, the sku on the subscription will be used to generate charges and orders. When sku_override is false, Recharge will dynamically fetch the sku from the corresponding shopify variant.
- use_shopify_variant_defaultsboolean
Flag instructing to pull the
price,sku,variant_title, andproduct_titlefrom the provided Shopify variant.You need to pass the
variant_idand set this attribute totruein the request for the flag to work. - statusstring
Status of the subscription. Can be used to cancel subscriptions when set to CANCELLED or to re-activate subscriptions when set to ACTIVE.
- variant_titlestring
The name of the product variant.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/42420080/subscriptions-bulk
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-d '{
"subscriptions":
[
{
"id": 64993717,
"price": 23.00,
"quantity": 3
},
{
"id": 64993718,
"price": 24.00,
"quantity": 4
},
{
"id": 64993719,
"price": 25.00,
"quantity": 5
}
]
}'{
"subscriptions": [
{
"id": 89560571,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "30",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-16T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "30",
"order_interval_unit": "day",
"price": 7,
"product_title": "Orange Juice Auto renew",
"properties": [],
"quantity": 2,
"recharge_product_id": 1463299,
"shopify_product_id": 4578081833063,
"shopify_variant_id": 32309455192167,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"variant_title": "Squeezed"
},
{
"id": 89560572,
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "6",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": 4,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-07-13T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "1",
"order_interval_unit": "month",
"price": 7,
"product_title": "Orange Juice Auto renew",
"properties": [],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 1463299,
"shopify_product_id": 4578081833063,
"shopify_variant_id": 32309455224935,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"variant_title": "Can"
},
{
"address_id": 48563471,
"analytics_data": {
"utm_params": []
},
"cancellation_reason": null,
"cancellation_reason_comments": null,
"cancelled_at": null,
"charge_interval_frequency": "4",
"created_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"customer_id": 43845860,
"email": "example@email.com",
"expire_after_specific_number_of_charges": null,
"has_queued_charges": 1,
"id": 89560574,
"max_retries_reached": 0,
"next_charge_scheduled_at": "2020-08-01T00:00:00",
"order_day_of_month": null,
"order_day_of_week": null,
"order_interval_frequency": "4",
"order_interval_unit": "week",
"price": 5,
"product_title": "Powder Milk 50.00% Off Auto renew",
"properties": [],
"quantity": 1,
"recharge_product_id": 1422079,
"shopify_product_id": 4546063663207,
"shopify_variant_id": 32165284479079,
"sku": null,
"sku_override": false,
"status": "ACTIVE",
"updated_at": "2020-07-10T10:39:00",
"variant_title": "1 / Powder"
}
]
}Bulk delete subscriptions
Bulk delete subscriptions.
There is a limit of 20 subscriptions per request.
Body Parameters
- idinteger* Required
Unique identifier of subscription.
- send_emailboolean
When your store setting indicates that cancellation emails should be sent, this value determines if subscription cancellation emails should be sent. If set to 1, cancellation emails will be sent for each of the specified subscriptions. If set to 0, cancellation emails will not be sent for any of the specified subscriptions.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE https://api.rechargeapps.com/addresses/42420080/subscriptions-bulk
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-d '{
"subscriptions":
[
{
"id": 64993717
},
{
"id": 64993718
},
{
"id": 64993719
}
],
"send_email":0
}'{
"subscriptions": []
}Webhook endpoints
Webhooks are a mechanism for reacting to specific events that are triggered in the Recharge system.
For example, a checkout completion, a customer activation or subscription cancellation. Webhooks will deliver you the data of the specific event in real-time. This data can be used to custom code logic behind automated subscription management, dashboards creation, discounts applying…
Retries / Idempotency
Due to webhook retries, it’s possible that your application receives the same webhook more than once. Ensure idempotency of the webhook call by detecting such duplicates within your application.
When a webhook is triggered, the payload will be identical to the payload you would receive from another API endpoint.
For example, a webhook on subscription/created event will be identical to the payload for retrieving a subscription by ID from the Recharge API.
There are a lot of things that can be done via Webhooks: It can be used to collect all kinds of data from our API and then create custom a Dashboard to show how much and when your customers are buying in real time, or use all this data to do Analytics of some kind in order to create a better customer experience. Webhooks can be used as a “Trigger” on your backend to update subscription products.
If you have some kind of a Subscription where you want to change the Product that the customer gets every month, you can do it by waiting for an order/created webhook on your backend, and when it fires you can make an API call to change the Product of that subscription or the next shipping date, etc.
## Respond to a webhook
Your webhook acknowledges that it received data by sending a 200 OK response. Any response outside of the 200 range will let Recharge know that you didn’t receive your webhook. Recharge has implemented a 5 second time-out period. We wait 5 seconds, if our system doesn’t get a response in that period we consider that request as failed. Our system will try 20 times to send the same webhook over the next 2 days, if the request fails every time our system will delete this webhook. At this moment our system is logging those deleted webhooks.
The Webhook object
These topics are deprecated, however they will not be removed from this API version: checkout/completed
Related guides: Extending webhook responses
Attributes
- idinteger
Unique numeric identifier for the webhook.
- addressstring
The URI where the webhook should send the POST request when the event occurs.
- included_objectsarray
Possible values: addresses, collections, customer, metafields
List of objects set to enrich the webhook payload. cf. extending responses
- topicstring
The event that will trigger the webhook.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"webhook": {
"id": 19451,
"address": "https://request.in/foo",
"included_objects": [],
"topic": "subscription/created",
"version": "2021-01"
}
}Available webhooks
The list of all available webhooks.
| Object | Topics | Scope Required |
|---|---|---|
Address |
address/created address/updated |
read_customers |
Async_batch |
async_batch/processed |
read_batches |
Customer |
customer/activated customer/created customer/deactivated customer/payment_method_updated customer/updated |
read_customers |
Charge |
charge/created charge/failed charge/max_retries_reached charge/paid charge/refunded charge/uncaptured charge/upcoming charge/updated |
read_orders |
Checkout |
checkout/created checkout/completed checkout/processed Note: Deprecated and not available for the Shopify integration with Shopify hosted Checkout (aka SCI) |
read_orders |
Onetime |
onetime/created onetime/deleted onetime/updated |
read_subscriptions |
Order |
order/cancelled order/created order/deleted order/processed order/upcoming order/updated |
read_orders |
Product |
product/created product/deleted product/updated |
read_products |
Subscription |
subscription/activated subscription/cancelled subscription/created subscription/deleted subscription/skipped subscription/updated subscription/unskipped subscription/paused |
read_subscriptions |
Shop |
app/uninstalled |
read_store |
Recharge |
recharge/uninstalled |
store_info |
Create a webhook
Create a webhook. Currently, only the API can be used to create a webhook.
To register a webhook endpoint for a specific object, you will need to have read permissions for that object on your Recharge API token. For example, if you want to register a webhook for subscription/created, you will need the read_subscriptions permissions.
Each API token can register a maximum of 10 webhooks of the same topic.
Related guides: Extending webhook responses
Body Parameters
- addressinteger* Required
The URI where the webhook should send the POST request when the event occurs.
- included_objectsarray
Possible values: addresses, collections, customer, metafields
List of objects to enrich the webhook payload. cf. extending responses
- topicinteger* Required
The event that will trigger the webhook.
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/webhooks' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{
"address": "https://request.in/foo",
"topic": "subscription/created"
}'{
"webhook": {
"id": 6,
"address": "https://request.in/foo",
"topic": "subscription/created",
"included_objects": [],
"version": "2021-01"
}
}Retrieve a webhook
Retrieve a webhook using the Recharge webhook id.
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/webhooks/19451' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"webhook": {
"id": 6,
"address": "https://request.in/foo",
"included_objects": [],
"topic": "subscription/created",
"version": "2021-01"
}
}Update a webhook
Updates Webhook
Related guides: Extending webhook responses
Body Parameters
- addressstring
The URI where the webhook should send the POST request when the event occurs.
- topicstring
The event that will trigger the webhook.
- included_objectsarray
Possible values: addresses, customer, collections, metafields
List of objects to enrich the webhook payload. cf. extending responses
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -X PUT 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/webhooks/19451' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{"address": "https://request.in/foo"}'{
"webhook": {
"id": 6,
"address": "https://request.in/foo",
"topic": "subscription/created",
"included_objects": [],
"version": "2021-01"
}
}Delete a webhook
Delete a Webhook
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -X DELETE 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/webhooks/19451' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{}List webhooks
Returns all the webhooks of the given store that are owned by the current requesting client (note that a a private token shows all of the store’s hooks, an integration token only shows that integration’s webhooks).
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/webhooks' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d limit=3 -G{
"webhooks": [
{
"id": 19451,
"address": "https://request.in/foo",
"included_objects": [
"metafields"
],
"topic": "subscription/created",
"version": "2021-01"
},
{
"id": 19452,
"address": "https://request.in/foo",
"included_objects": [],
"topic": "subscription/cancelled",
"version": "2021-11"
},
{
"id": 19453,
"address": "https://request.in/foo",
"included_objects": [],
"topic": "subscription/updated",
"version": "2021-01"
}
]
}Test webhooks
In order to test webhook connectivity, you can trigger the dispatch of a test webhook with our webhook test endpoint. Sending a POST request to the webhook endpoint containing a webhook id will dispatch an empty webhook body to the specified webhook’s destination url.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/webhooks/<webhook_id>/test' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{}'{}Webhooks explained
Here you will find what specific action triggers a given webhook.
Address webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Customers enabled ( read_customer ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
address/created |
This will trigger when you create an address via API, or when you go through the checkout with a particular address for the first time with the same customer. |
address/updated |
This will trigger when you update an address via API, or when you update the address via UI. It will also trigger whenever a subscription has been activated or cancelled. |
Charge webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Orders enabled ( read_orders ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
charge/created |
This will trigger when a charge is created. |
charge/failed |
This will trigger every time we try to process a charge and it fails due to various reasons (insufficient funds, invalid CC info, expired CC, etc.) on both API and UI. |
charge/max_retries_reached |
This will trigger after we attempt to process a charge 8 times, and it failed every time due to various CC issues. This can be triggered on both UI (manually retry a charge 8 times and fail) and API. |
charge/paid |
This will trigger when a charge is successfully processed, both manually via UI and automatic recurring charge. This will not trigger on the checkout itself. |
charge/refunded |
This will trigger when a charge is successfully refunded, either partially or in full. It will fire if a charge has been refunded both manually via UI and through an API request. |
charge/upcoming |
This will trigger X days before the upcoming charge is scheduled. The default is 3 days but your store specific setting can be verified on the Notification Settings page in the description of the Upcoming charge customer notification. |
charge/updated |
This will trigger when applying a discount, a change to charge that recalculates shipping rates as well as if next_charge_date is updated on charge endpoint charges/<charge_id>/change_next_charge_date. |
charge/deleted |
This will trigger when a subscription is cancelled and upcoming charges are deleted. |
Checkout webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Orders enabled ( read-orders ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
checkout/created |
This will trigger when a checkout is successfully created. |
checkout/completed |
Will be deprecated. |
checkout/processed |
This will trigger when a checkout is successfully processed. |
checkout/updated |
This will trigger when a checkout is successfully updated. |
Customer webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Customers enabled ( read_customers ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
customer/activated |
This will trigger when you activate* a customer * activating means that you have added a subscription to a customer who didn’t have an active subscription previously. |
customer/created |
This will trigger when you create a customer via API or go through the checkout with a particular email address for a first time customer. |
customer/deactivated |
This will trigger when the last subscription a customer had expires, so he no longer has ANY active subscriptions (which means there are no QUEUED charges/orders for this customer). |
customer/payment_method_updated |
This will trigger only* when you update the payment_token from the UI * We are working on triggering this when you do the update from the API as well. |
customer/updated |
This will trigger when you update a customer via both API and UI. |
customer/deleted |
This will trigger when you delete a customer via both API and UI. |
Onetime webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Subscriptions enabled ( read_subscriptions ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
onetime/created |
This will trigger when you create a one time product via API. |
onetime/deleted |
This will trigger when you delete a one time product via API. |
onetime/updated |
This will trigger when you update a one time product via API. |
Order webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Orders enabled ( read_orders ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
order/created |
This will trigger when an order is created (when a charge is successfully processed) * In case of prepaid Orders the order/created webhooks will be fired for each prepaid order that is created. This occurs on the date the order is scheduled at. |
order/deleted |
This will trigger when an order is deleted. |
order/processed |
This will trigger when the order is processed (when an order goes from status queued to status success). This will not trigger on checkout. |
order/upcoming |
This will trigger X days before a QUEUED (prepaid) order is scheduled to be processed. The default is 3 days. |
order/updated |
This will trigger when an order is updated. |
Plan webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Products enabled ( read_products ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
plan/created |
This will trigger when a plan is created by one of the following methods: via API, via Merchant portal or when using the 2021-01 Products endpoint. |
plan/deleted |
This will trigger when a plan is deleted by one of the following methods: via API, via Merchant portal or when using the 2021-01 Products endpoint. |
plan/updated |
This will trigger when a plan is updated by one of the following methods: via API, via Merchant portal or when using the 2021-01 Products endpoint… |
Subscription webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Subscriptions enabled ( read_subscriptions ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
subscription/activated |
This will trigger when you activate a subscription via API or UI. |
subscription/cancelled |
This will trigger when you cancel a subscription via API or UI. An involuntary subscription cancelled due to max retries reached will only trigger the charge/max_retries_reached webhook and not the subscription/cancelled webhook. |
subscription/created |
This will trigger when you create a subscription via API or when you go through the checkout on UI. |
subscription/deleted |
This will trigger when you delete a subscription via API or UI. |
subscription/skipped |
This will trigger when you skip a subscription within a charge, meaning that you only skip a particular subscription (the subscription_id you send in the body) in that charge if there are multiple subscriptions related to that charge. |
subscription/unskipped |
This will trigger when you unskip a subscription within a charge, meaning you only unskip a particular subscription (the subscription_id you send in the body) in that charge if there are multiple subscriptions related to that charge. |
subscription/updated |
This will trigger when you update a subscription via API (PUT method) or when you update the subscription via UI. This will also trigger when you update next charge date on Customer Portal, or when you change it using subscription endpoint subscriptions/ <subscription_id>set_next_charge_date. |
subscription/swapped |
This will trigger when you swap a subscription product for a given address to a different product or product variation API or UI. |
subscription/paused |
This will trigger when a customer pauses a subscription from within the customer portal. |
Other webhooks
To use these webhooks your API Token must have read permissions for Store enabled ( read_store ).
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
app/uninstalled |
This will trigger when you uninstall OAuth app on your store. |
recharge/uninstalled |
This will trigger when Recharge is uninstalled. |
store/updated |
This will trigger when and update has been made to the store. |
Webhook validation
Webhooks created through the API can be verified by calculating a digital signature. Each Webhook request includes an X-Recharge-Hmac-Sha256 header which is generated using the API Client Secret, along with the data sent in the request.
API Client Secret is not the same as your API token and it can be found at:
Recharge Dashboard—>Integrations—>API Tokens—>Click on your token
Edit API Token page will appear and there you will find API Client Secret
The request_body must be in JSON string format. Validation will fail even if one space is lost in process of JSON string generation.
Then use code similar to the example by adapting it to the programming language that you are using for your project.
Related guides: Example code for validating webhooks
Async batch endpoints
The Async batches API can be used for processing large volumes of operations asynchronously, in order to reduce aggregate processing time and network traffic when interacting with many unique objects. For example, a user can leverage async_batches to create 1000 discounts with only 3 API requests.
As shown in the diagram below, the necessary steps to create and process a batch are:
1. Create an async_batch with the desired batch_type
2. Add tasks (individual operations) to your batch. You can add up to 1,000 tasks with each request, up to 10,000 tasks per batch.
3. Submit the batch for processing. Until a batch is submitted for processing, no tasks are attempted.
4. You may retrieve the batch to view progress details while it processes, or register for the async_batch/processed webhook to receive immediate notification of batch completion.
5. Page through the tasks in the batch to view results of each completed or failed task.
Related guides: Examples of Async batches 
The Async batch object
Attributes
- batch_typestring
Possible values: address_discount_apply, address_discount_remove, discount_create, discount_delete, discount_update, product_create, product_update, product_delete, onetime_create, onetime_delete, bulk_subscriptions_create, bulk_subscriptions_update, bulk_subscriptions_delete, subscription_cancel
Indicates the object type and operation required for all tasks in a batch
Batches will only leverage resources from the same version they are created in. e.g. a batch created with
2021-11will only process tasks from the2021-11version. - closed_atstring
Indicates the date and time that processing was completed for a batch
- created_atstring
Indicates the date and time a batch was created
- fail_task_countstring
Indicates the number of failed tasks in a batch, during or after processing
- idstring
Unique identifier of the batch, used for adding tasks to a batch and to initiate batch processing
- statusstring
Indicates the status of the batch. Available statuses are not_started, processing, completed, failed
- submitted_atstring
Indicates the date and time that a batch was triggered to process
- success_task_countstring
Indicates the number of successful tasks in a batch, during or after processing.
- total_task_countstring
Indicates the total number of tasks in a batch
- updated_atstring
Indicates the date and time at which a batch was last updated
- versionstring
Indicates the date and time at which a batch was last updated
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"async_batch": {
"id": 19,
"batch_type": "desired_batch_type",
"closed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-06-05T08:52:10",
"deleted_at": null,
"fail_task_count": 0,
"status": "not_started",
"submitted_at": null,
"success_task_count": 0,
"total_task_count": 0,
"updated_at": "2020-06-05T08:52:10",
"expired_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00"
}
}Create a batch
In order to create, retrieve, or process batches, the API token requires the write_batches permission. Additional permissions are required, dependent upon the indicated batch_type. For example, for a batch type of discount_create, the API token requires the write_discounts permission.
Create a new batch, and indicate the desired outcome of the batch using batch_type.
CAUTION - Async batches and their tasks will only be retained in Recharge for one month after batch creation.
Available batch types
The async_batches API supports many functions, each identified as a batch_type. Typically, the task body for a batch_type will be representative of a single request to our standard endpoints, however, some variations may be present.
Related guides: Examples of Async Batches
Batches will only leverage resources from the same version they are created in. e.g. a batch created with 2021-11 will only process tasks from the 2021-11 version.
Body Parameters
- batch_typestring
Possible values: address_discount_apply, address_discount_remove, change_next_charge_date, discount_create, discount_delete, discount_update, product_create, product_update, product_delete, onetime_create, onetime_delete, bulk_subscriptions_create, bulk_subscriptions_update, bulk_subscriptions_delete, subscription_cancel
Desired batch type
More Parameters
Responses
- 201
Success
Show response object
curl -i -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-H "Accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X POST https://api.rechargeapps.com/async_batches \
--data '{ "batch_type": "desired_batch_type"}'{
"async_batch": {
"id": 19,
"batch_type": "desired_batch_type",
"closed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-06-05T08:52:10",
"deleted_at": null,
"fail_task_count": 0,
"status": "not_started",
"submitted_at": null,
"success_task_count": 0,
"total_task_count": 0,
"updated_at": "2020-06-05T08:52:10",
"expired_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"version": "2021-01"
}
}Retrieve a batch
Retrieve a batch using the Recharge batch id. A batch can be retrieved during processing to evaluate batch progress.
## HTTP request examples
GET /async_batches/<batch_id>
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -i -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-H "Accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X GET 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/async_batches/16'{
"async_batch": {
"id": 19,
"batch_type": "desired_batch_type",
"closed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-06-05T08:52:10",
"deleted_at": null,
"fail_task_count": 0,
"status": "not_started",
"submitted_at": null,
"success_task_count": 0,
"total_task_count": 0,
"updated_at": "2020-06-05T08:52:10",
"expired_at": "2020-07-15T00:00:00",
"version": "2021-01"
}
}List batches
Returns a list of all your async_batches.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -i -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'
-H "Accept: application/json"
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-X GET https://api.rechargeapps.com/async_batches{
"async_batches": [
{
"id": 20,
"batch_type": "discount_delete",
"closed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-06-05T09:21:37",
"deleted_at": null,
"fail_task_count": 0,
"status": "not_started",
"submitted_at": null,
"success_task_count": 0,
"total_task_count": 40,
"updated_at": "2020-06-05T09:21:37",
"version": "2021-01"
},
{
"id": 19,
"batch_type": "discount_create",
"closed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-06-05T08:52:11",
"deleted_at": null,
"fail_task_count": 0,
"status": "not_started",
"submitted_at": null,
"success_task_count": 0,
"total_task_count": 0,
"updated_at": "2020-06-05T08:52:11",
"version": "2021-01"
},
{
"id": 16,
"batch_type": "discount_create",
"closed_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:14:45",
"deleted_at": null,
"fail_task_count": 0,
"status": "completed",
"submitted_at": "2020-05-29T09:21:33",
"success_task_count": 2000,
"total_task_count": 2000,
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07",
"version": "2021-01"
}
]
}Process a batch
Until a batch is submitted for processing, no tasks are attempted. Once you have ensured the tasks in a batch are ready for processing, you can submit for processing using this endpoint and the associated batch id.
Webhooks - Batches process quickly, and may result in Recharge dispatching many webhooks at a high rate. Ensure any systems subscribed to resulting webhooks are capable of handling such load.
Responses
- 201
Success
Show response object
curl -X POST 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/async_batches/21/process' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-d '{}'{
"async_batch": {
"id": 21,
"batch_type": "discount_create",
"closed_at": null,
"created_at": "2020-06-05T10:53:36",
"deleted_at": null,
"fail_task_count": 0,
"status": "processing",
"submitted_at": "2020-06-05T10:54:54",
"success_task_count": 0,
"total_task_count": 10,
"updated_at": "2020-06-05T10:54:54"
}
}Async batch tasks
Most commonly, the response from listing tasks on an async_batch id will be identical to the body of a singular request to standard Recharge API endpoints. However, in some instances there are variations from the standard list task response body. See below for examples corresponding to each batch_type.
Related guides: Examples of async batches
The Async batch tasks object
Attributes
- batch_idinteger
Indicates the batch that the task is contained by
- bodyobject
This object contains the body of a standard API request. For example, when creating discounts with a discount_create batch, this parameter contains a standard body for POST /discounts
- completed_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time a task was completed
- created_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time that a task was created and added to the batch
- deleted_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time that a task was deleted from the batch
- idinteger
Unique identifier for the task within a batch
- queued_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time a task was queued for processing within batch processing
- resultstring
Contains the individual response body for the task
- started_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time a task was processed
- statusstring
Possible values: pending, processing, failed, success
Indicates the status of the task within a batch.
- updated_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time a task was most recently updated
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"async_batch_tasks": [
{
"id": 22048,
"batch_id": 16,
"body": {
"code": "19476193",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
},
"completed_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:19:38",
"deleted_at": null,
"queued_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"result": {
"output": {
"discount": {
"id": 28288390,
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ALL",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": true
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": true
}
},
"code": "19476193",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"duration_usage_limit": null,
"ends_at": null,
"first_time_customer_restriction": null,
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": null,
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"usage_limit": null,
"value": 100
}
},
"status_code": 200
},
"started_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"status": "success",
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07"
},
{
"id": 22047,
"batch_id": 16,
"body": {
"code": "28831178",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
},
"completed_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:19:38",
"deleted_at": null,
"queued_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"result": {
"output": {
"discount": {
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ALL",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": true
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": true
}
},
"code": "28831178",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"duration_usage_limit": null,
"ends_at": null,
"first_time_customer_restriction": null,
"id": 28288389,
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": null,
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"usage_limit": null,
"value": 100
}
},
"status_code": 200
},
"started_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"status": "success",
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07"
},
{}
]
}Create a batch task
A batch contains operations of similar type (indicated by batch_type), called tasks. A task is typically representative of a single API request, with a body parameter containing the standard request body for the associated batch_type. A single request to add tasks may contain up to 1,000 tasks, and a batch may contain up to 10,000 tasks.
##HTTP examples
POST /async_batches/<batch_id>/tasks
Batches will only leverage resources from the same version they are created in. e.g. a batch created with 2021-11 will only process tasks from the 2021-11 version.
Body Parameters
- batch_idinteger
Indicates the batch that the task is contained by
- bodyobject
This object contains the body of a standard API request. For example, when creating discounts with a discount_create batch, this parameter contains a standard body for POST /discounts
- completed_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time a task was completed
- created_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time that a task was created and added to the batch
- deleted_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time that a task was deleted from the batch
- idinteger
Unique identifier for the task within a batch
- queued_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time a task was queued for processing within batch processing
- resultstring
Contains the individual response body for the task
- started_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time a task was processed
- statusstring
Possible values: pending, processing, failed, success
Indicates the status of the task within a batch.
- updated_atdatetime
Indicates the date and time a task was most recently updated
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
Success
Show response object
curl -i -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-H "Accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X POST 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/async_batches/21/tasks' \
--data '{
"tasks": [
{
"body": {
"code": "indexing",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "maroon",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "web services",
"value": 100,
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled"
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "PCI",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "Cheese",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "overriding",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "bandwidth-monitored",
"value": 100,
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled"
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "Falkland Islands (Malvinas)",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "Computer",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
}
},
{
"body": {
"code": "digital",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
}
}
]
}'{
"count": 10
}List batch tasks
Returns a list of all tasks in the indicated batch, using batch id. For batches with many tasks, pagination is supported when listing tasks. Use this function to evaluate the task-level results of a batch during, or after processing. Task results will be contained in the results object of each task.
Query Parameters
- idsstring
Filter tasks by id. If passing multiple values, must be comma separated. Non-integer values will result in a 422 error
More Parameters
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl -i -H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token' \
-H "Accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X GET 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/async_batches/16/tasks'{
"async_batch_tasks": [
{
"id": 22048,
"batch_id": 16,
"body": {
"code": "19476193",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
},
"completed_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:19:38",
"deleted_at": null,
"queued_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"result": {
"output": {
"discount": {
"id": 28288390,
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ALL",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": true
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": true
}
},
"code": "19476193",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"duration_usage_limit": null,
"ends_at": null,
"first_time_customer_restriction": null,
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": null,
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"usage_limit": null,
"value": 100
}
},
"status_code": 200
},
"started_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"status": "success",
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07"
},
{
"id": 22047,
"batch_id": 16,
"body": {
"code": "28831178",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"status": "enabled",
"value": 100
},
"completed_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:19:38",
"deleted_at": null,
"queued_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"result": {
"output": {
"discount": {
"applies_to": null,
"applies_to_id": null,
"applies_to_product_type": "ALL",
"applies_to_resource": null,
"channel_settings": {
"api": {
"can_apply": true
},
"checkout_page": {
"can_apply": true
},
"customer_portal": {
"can_apply": true
},
"merchant_portal": {
"can_apply": true
}
},
"code": "28831178",
"created_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"discount_type": "shipping",
"duration": "forever",
"duration_usage_limit": null,
"ends_at": null,
"first_time_customer_restriction": null,
"id": 28288389,
"once_per_customer": false,
"prerequisite_subtotal_min": null,
"starts_at": null,
"status": "enabled",
"times_used": 0,
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"usage_limit": null,
"value": 100
}
},
"status_code": 200
},
"started_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:06",
"status": "success",
"updated_at": "2020-05-29T09:23:07"
},
{}
]
}Token information
This resource allows a caller to inspect basic information regarding the token in use. It will only return a single object related to the calling token ( ie - a call with api_token.id=1 will only return information regarding api_token.id=1.
The Token information object
Object containing a token’s information.
Attributes
- clientobject
Details of the client which generated the token.
If the API token was generated by an OAuth app, the object will contain associated client information.
If the API token was generated by the merchant, the object will reflect thenameprefaced by ‘[Private App]’ andcontact_emailof the token.Show object attributes - contact_emailstring
The email associated with the API Token record.
For tokens created via OAuth App the contact can be
null - namestring
The name of the API Token as created by merchant.
- scopesarray
A list of scopes on the API Token.
Error related attributes
More Attributes
{
"client": {
"name": "PARTNER",
"contact_email": "ed@partner.com"
},
"contact_email": "jbluhm@example.com",
"name": "token name",
"scopes": [
"read_store",
"write_payment_methods"
]
}Retrieve token information
Retrieve token details.
Responses
- 200
successful response
Show response object
curl 'https://api.rechargeapps.com/token_information' \
-H 'X-Recharge-Access-Token: your_api_token'{
"token_information": {
"name": "token name",
"client": {
"name": "PARTNER",
"contact_email": "ed@partner.com"
},
"contact_email": "jbluhm@example.com",
"scopes": [
"read_shop",
"write_payments"
]
}
}